Both large and small companies spend huge amounts of money to be sure: their network resources and Internet connections are used for their intended purpose. Companies hire the best IT professionals, but even the most technically unenlightened user can find a tricky way to bypass firewall policies and gain access to blocked websites. In this article, the author describes how an anonymizer or anonymizing proxy allows you to bypass firewall policies and jeopardize the three main properties of enterprise information security: confidentiality, accessibility, and integrity. But on the other hand, anonymizer can also be beneficial: it helps to hide your IP address when surfing the web.
1. Introduction
1.1. Dilemma
Both large and small companies spend huge amounts of money to be sure: their network resources and Internet connections are used for their intended purpose. Companies hire the best IT professionals, but even the most technically unenlightened user can find a tricky way to bypass firewall policies and gain access to blocked websites. This article describes how an anonymizer or anonymizing proxy allows you to bypass firewall policies and jeopardize the three main properties of enterprise information security: confidentiality, accessibility, and integrity. But on the other hand, anonymizer can also be beneficial: it helps to hide your IP address when surfing the web.
1.2. Introductory information
Anonymizers (or anonymizing proxies) are software products and services that can bring both benefit and harm. Anonymizers provide the ability to anonymously surf the network by spoofing the user's real IP address. Anonymizers can also bypass security filters set by firewall policies (ACLs) and gain access to banned websites or transmit information without the organization’s knowledge, thereby violating the three main properties of information security.
All the user needs to do is install the proxy application and configure the proxy address in the web browser. Then, when trying to access the website, the computer connects to the proxy server, bypasses the firewall policies and enters the blocked site.
The first anonymizer, Anonymizer.com, was developed in 1997 by Lance Cotrell while working on his dissertation in astrophysics at the University of California, San Diego. Cottrell advocated online anonymity, and it was he who founded the Kosovo Privacy Project, which allows users to anonymously and with impunity report on the events of the 1999 Kosovo War (Cottrell, 2011).
With the growing popularity of the Internet, more and more people see the network as the main source of information. The role of communication services is also growing: email, chat, instant messaging (IM), social networks (Facebook, Twitter). E-commerce and online banking are two other areas that have changed the way users conduct business and manage their personal data. Many websites today collect information about exactly what resources a user visits when traveling on the global web. Almost everything is recorded: starting from the user's IP address, ending with how much time he spent on a particular site. Each mouse click on the site brings valuable (and in terms of money, too) information that interested companies are willing to pay for. Many people already know that information about them is collected, stored in cookies, and then sent to commercial and advertising companies such as DoubleClick or Adbot. Cautious users include anonymizing software and services to maintain confidentiality and disguise their real location and IP address. Another reason to mask an IP address is because masking adds another layer of protection against hackers when surfing the net. However, the anonymizer has some side effects, and inventive users willingly took advantage of these effects: the anonymizer allows you to bypass the corporate firewall and gain access to blocked sites.
Figure 1 shows how a firewall blocks a site.
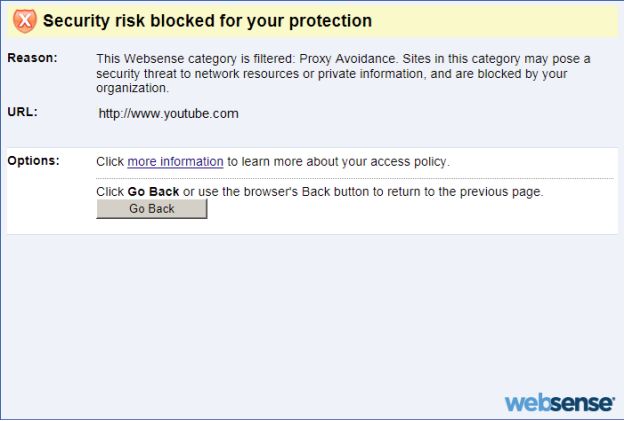
Figure 1. Warning
Figure 2 shows how the anonymizer bypasses the firewall rules.
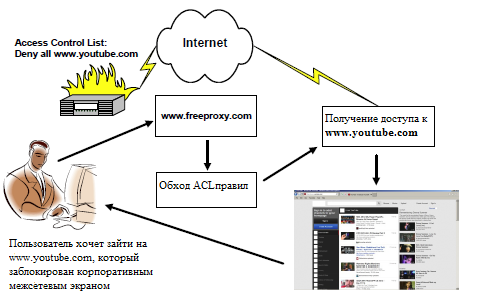
Figure 2. Bypass ACL rules
2. Principles of work
2.1. Anonymizer example
The workstation in the network is usually connected to the switch, and the switch to the router. On the router, a firewall or proxy server can be configured to prevent unauthorized connections. Figure 3 shows the situation when a user tries to open the site [DLMURL] https://www.youtube.com [/ DLMURL] from his workstation. The ACL rules prescribe access to [DLMURL] https://www.youtube.com [/ DLMURL], therefore, the user will be able to access the desired site.
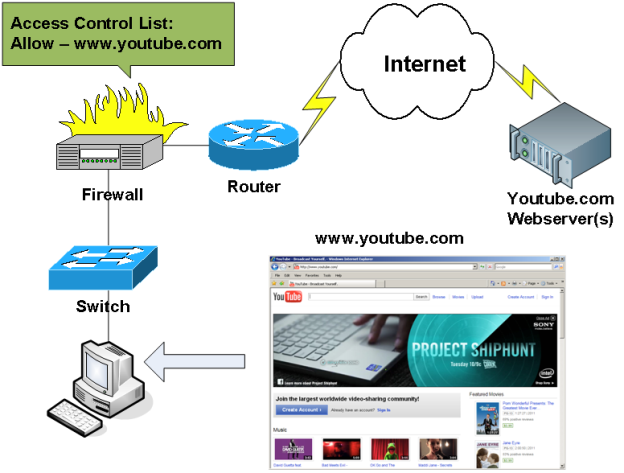
Figure 3. Allowed websites
Figure 4 shows the opposite situation: access to [DLMURL] https://www.youtube.com [/ DLMURL] is denied. The firewall will block the connection, and the corresponding message will appear in the user's web browser.
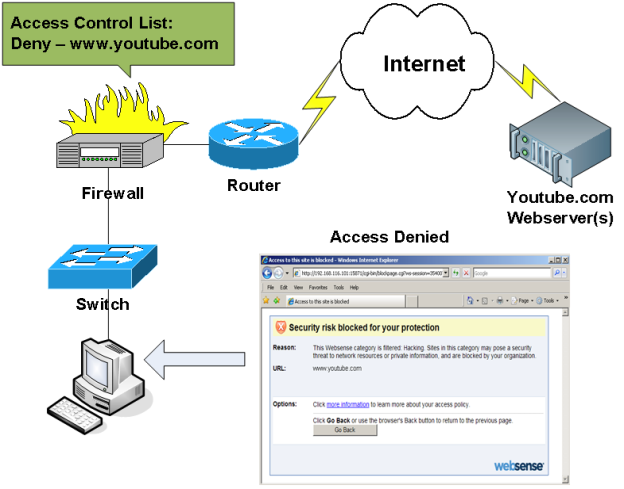
Figure 4. Denied websites
Figure 5 shows the situation when a user used the Internet anonymizer (proxy server) to access [DLMURL] https://www.youtube.com [/ DLMURL]. A computer with an anonymizer establishes a secure connection, which allows the user to bypass ACL rules and freely surf the network unnoticed by the firewall. As a result, the firewall does not even suspect that the user is accessing blocked websites.
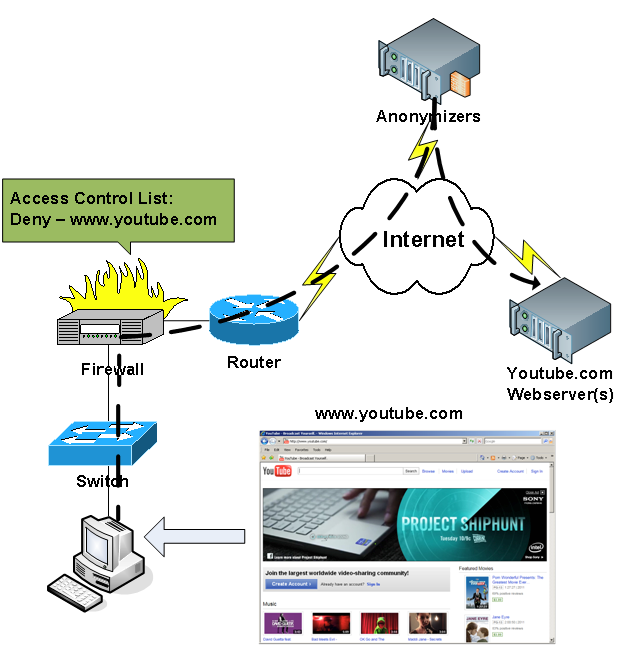
Figure 5. Access to a restricted site through anonymizer
2.2. How to implement the plan
There are many applications and anonymizing services. Some of them are distributed free of charge (for example, proxify.com), others will have to pay. JonDonym, for example, has a monthly subscription fee, the size of which depends on the amount of traffic. As an example for this article, the free version of the anonymizing proxy server JonDonym - (JAP) AN.ON.
(JAP) AN.ON is a research, free distributed project. The application is written in Java, so AN.ON (JAP) can be installed on various operating systems, including Windows, Macintosh, OS / 2, Linux / UNIX, etc.
JAP allows you to surf the net anonymously and discreetly. JAP proxies are located all over the world (JAP, 2012). You can download JAP from the site https://anon.inf.tu-dresden.de/index_en.html (see Appendix A). After downloading, follow the installation process (see Appendix B).
2.3. Blocked Websites
Companies customize their firewalls based on many factors. One of the factors is the prevention of attacks on the company's network resources. Another factor is restricting access by internal users to inappropriate or malicious websites.
In the following example, the corporate firewall denies access to the site https://www.anonymizer.com . When a user tries to open the specified site, the warning “Security risk blocked for your protection” appears in his browser window, and access to the site will be denied, see Figure 6.
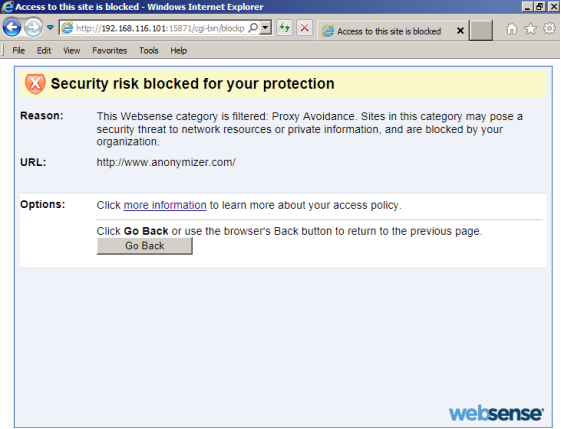
Figure 6. Firewall warning about a blocked site
Determine your IP address settings. Open Windows Internet Explorer and enter [DLMURL] https://www.whatismyip.com [/ DLMURL] in the address bar. Your IP address will be displayed on the site: 45.112.164.5 (the address has been changed for security reasons), see Figure 7 (Whatismyip.com, 2012).
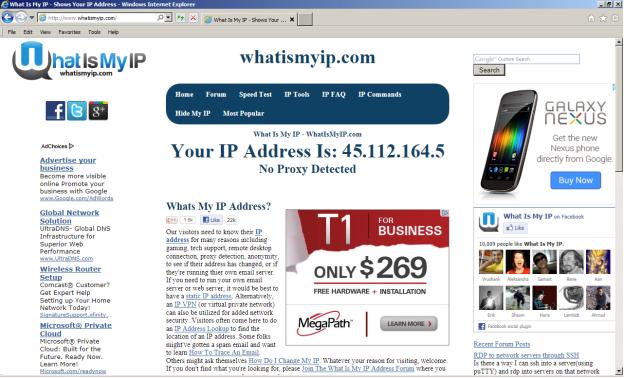
Figure 7. Defining an IP Address
2.4. JAP launch
To disguise your IP address, run and configure the JAP application.
Step 1: Click on the JAP application icon to start the program, see Figure 8.

Figure 8. JAP application icon
Step 2: To enable the anonymity service, click on the “On” radio button, see Figure 9.
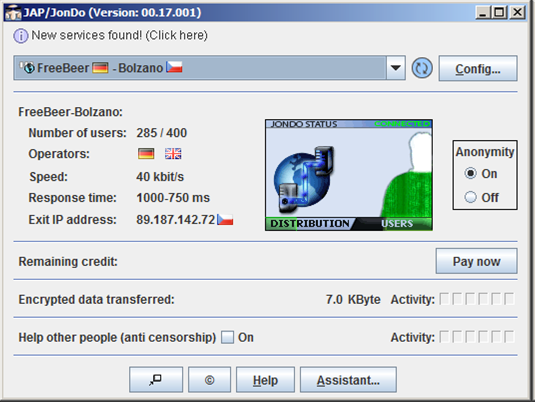
Figure 9. JAP application interface
Step 3: From the drop-down list, select the location and anonymization server: “FreeBee-Bozlano”, see Figure 10.
Figure 10. Choosing an anonymization server
Step 4: Configure Windows Internet Explorer to use a proxy. Open Internet Explorer, click “Tools”, and then “Internet Options”, see Figure 11.
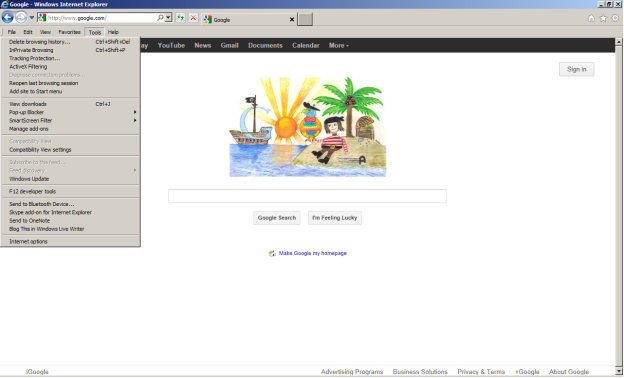
Figure 11. Configuring the proxy server in a web browser
Step 5: In the “Internet Options” window, select the “Connections” tab, and then click on the “LAN settings” button, see Figure 12.
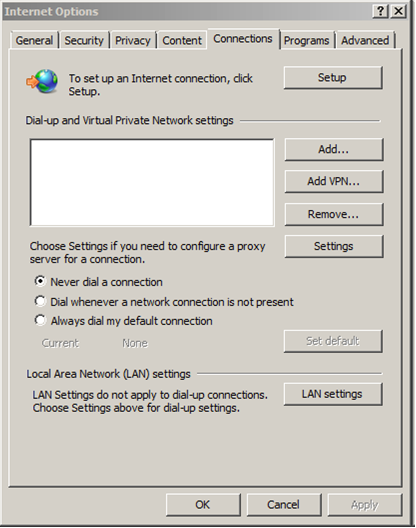
Figure 12. Selecting LAN settings
Step 6: In the “Proxy server” field, check “Use a proxy server for your LAN”. Enter “localhost” in the address field and “4001” in the port field. To complete the setup, click the “OK” button and close the “Internet Options” window, see Figure 13.
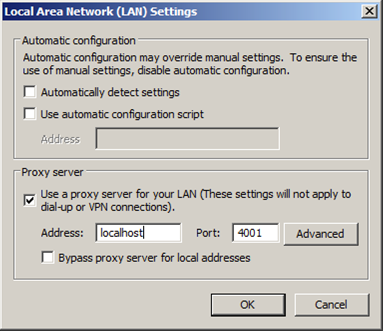
Figure 13. Configuring the IP address and proxy port
Note: Uncheck “Use a proxy server for your LAN” when you are not working with a proxy server, otherwise normal connections will not be established.
Step 7: Test the proxy server settings. Open Internet Explorer again and enter [DLMURL] https://www.whatismyip.com [/ DLMURL] in the address bar. Now your IP address is not 45.112.164.5, but 178.33.255.188, and you are not in the United States, but in France, see Figure 14 (Whatismyip.com, 2012).
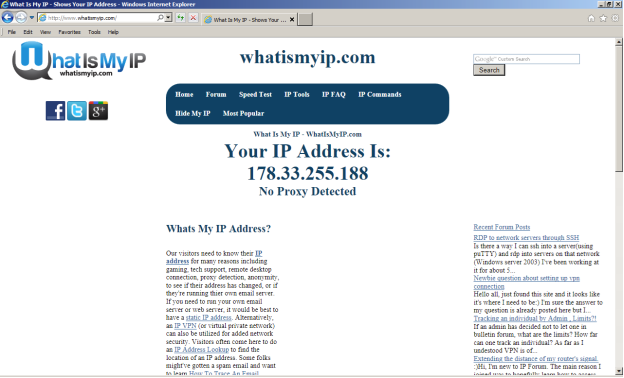
Figure 14. Checking the IP address with proxy enabled
2.5. Access blocked websites
Now in the address bar of Internet Explorer, enter the URL https://www.anonymizer.com . Now the firewall does not block the site, and we do not see any warning messages in the browser window, see Figure 15 (Anonymizer.com, 2012).
Figure 15. Accessing a blocked website using a proxy
References
Lance Cottrell, From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, (October 2, 2011). Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lance_Cottrell [/ DLMURL]
EC-Council Press, Ethical Hacking and Countermeasures, Cengage Learning (2010) Livinginternet.com, How Anonymizers Work Retrieved from https://www.livinginternet.com/i/is_anon_work.htm (2012)
Anonymizer.com, knowledgecenter, Retrieved from https://www.anonymizer.com/knowledgecenter (2012)
Fred Hapgood, Web Monitoring: Anonymizers vs. Anti-Anonymizers, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://www.csoonline.com/artic...nonymizers [/ DLMURL] (2008)
JAP, Protection of Privacy on the Internet, Retrieved from Link is not valid. de / index_en.html (2012)
JonDonym, Private and Secure Web Surfing, Retrieved from Link is not valid. net / (2012)
What is My IP, Shows Your IP Address, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://whatismyip.com [/ DLMURL] (2012) Proxify, Proxify® anonymous proxy protects your online privacy, Retrieved from https://proxify.com (2012)
Carolyn Pearson, The “Great Firewall” of China, A Real National Strategy to Secure Cyberspace ?, GIAC practical repository (2004)
Wireshark, The world's foremost network protocol analyzer, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://www.wireshark.org/ [/ DLMURL] (2012)
Websense, V-Series appliance, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://www.websense.com/content/appliances.aspx [/ DLMURL] (2012)
Network Chemistry, Inc., Packetyzer Software, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://www.gotoassist.com [/ DLMURL] (2012)
Informer Technologies, Inc., Software.informer, Network Chemistry Packetyzer, Retrieved from http: //network-chemistry-packetyzer.sof ... former.com (2012)
Microsoft Support, The Basics of Reading TCP / IP Trace, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://support.microsoft.com/kb/169292 [/ DLMURL] (2012)
Cisco, Cisco IPS 4200 Series Sensors, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://www.cisco.com/en/US/pro...ps9157/pro [/ DLMURL] duct_data_sheet09186a008014873c_ps4077_Products_Data_Sheet.html (2012)
Nevis Network, An Architectural View of LAN Security: In-Band versus Out-of-Band Solutions, Retrieved from https://www.nevisnetworks.com/content/wh ... ers / Inband% 20vs% 20 Out-of-band .pdf (2007)
Sourcefire, Snort, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://www.snort.org/ [/ DLMURL] (2012)
John Brozycki, Detecting and Preventing Anonymous Proxy Usage, [DLMURL] https://Sans.org [/ DLMURL], Reading Room (2008)
Nicholas Pappas, Network IDS & IPS Deployment Strategies, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://www.sans.org/reading_ro...egies_2143 [/ DLMURL] (2008)
[DLMURL="https://www.securitylab.ru/analytics/436174.php"] Source [/ DLMURL] via SPKR Forum
1. Introduction
1.1. Dilemma
Both large and small companies spend huge amounts of money to be sure: their network resources and Internet connections are used for their intended purpose. Companies hire the best IT professionals, but even the most technically unenlightened user can find a tricky way to bypass firewall policies and gain access to blocked websites. This article describes how an anonymizer or anonymizing proxy allows you to bypass firewall policies and jeopardize the three main properties of enterprise information security: confidentiality, accessibility, and integrity. But on the other hand, anonymizer can also be beneficial: it helps to hide your IP address when surfing the web.
1.2. Introductory information
Anonymizers (or anonymizing proxies) are software products and services that can bring both benefit and harm. Anonymizers provide the ability to anonymously surf the network by spoofing the user's real IP address. Anonymizers can also bypass security filters set by firewall policies (ACLs) and gain access to banned websites or transmit information without the organization’s knowledge, thereby violating the three main properties of information security.
All the user needs to do is install the proxy application and configure the proxy address in the web browser. Then, when trying to access the website, the computer connects to the proxy server, bypasses the firewall policies and enters the blocked site.
The first anonymizer, Anonymizer.com, was developed in 1997 by Lance Cotrell while working on his dissertation in astrophysics at the University of California, San Diego. Cottrell advocated online anonymity, and it was he who founded the Kosovo Privacy Project, which allows users to anonymously and with impunity report on the events of the 1999 Kosovo War (Cottrell, 2011).
With the growing popularity of the Internet, more and more people see the network as the main source of information. The role of communication services is also growing: email, chat, instant messaging (IM), social networks (Facebook, Twitter). E-commerce and online banking are two other areas that have changed the way users conduct business and manage their personal data. Many websites today collect information about exactly what resources a user visits when traveling on the global web. Almost everything is recorded: starting from the user's IP address, ending with how much time he spent on a particular site. Each mouse click on the site brings valuable (and in terms of money, too) information that interested companies are willing to pay for. Many people already know that information about them is collected, stored in cookies, and then sent to commercial and advertising companies such as DoubleClick or Adbot. Cautious users include anonymizing software and services to maintain confidentiality and disguise their real location and IP address. Another reason to mask an IP address is because masking adds another layer of protection against hackers when surfing the net. However, the anonymizer has some side effects, and inventive users willingly took advantage of these effects: the anonymizer allows you to bypass the corporate firewall and gain access to blocked sites.
Figure 1 shows how a firewall blocks a site.

Figure 1. Warning
Figure 2 shows how the anonymizer bypasses the firewall rules.

Figure 2. Bypass ACL rules
2. Principles of work
2.1. Anonymizer example
The workstation in the network is usually connected to the switch, and the switch to the router. On the router, a firewall or proxy server can be configured to prevent unauthorized connections. Figure 3 shows the situation when a user tries to open the site [DLMURL] https://www.youtube.com [/ DLMURL] from his workstation. The ACL rules prescribe access to [DLMURL] https://www.youtube.com [/ DLMURL], therefore, the user will be able to access the desired site.

Figure 3. Allowed websites
Figure 4 shows the opposite situation: access to [DLMURL] https://www.youtube.com [/ DLMURL] is denied. The firewall will block the connection, and the corresponding message will appear in the user's web browser.

Figure 4. Denied websites
Figure 5 shows the situation when a user used the Internet anonymizer (proxy server) to access [DLMURL] https://www.youtube.com [/ DLMURL]. A computer with an anonymizer establishes a secure connection, which allows the user to bypass ACL rules and freely surf the network unnoticed by the firewall. As a result, the firewall does not even suspect that the user is accessing blocked websites.

Figure 5. Access to a restricted site through anonymizer
2.2. How to implement the plan
There are many applications and anonymizing services. Some of them are distributed free of charge (for example, proxify.com), others will have to pay. JonDonym, for example, has a monthly subscription fee, the size of which depends on the amount of traffic. As an example for this article, the free version of the anonymizing proxy server JonDonym - (JAP) AN.ON.
(JAP) AN.ON is a research, free distributed project. The application is written in Java, so AN.ON (JAP) can be installed on various operating systems, including Windows, Macintosh, OS / 2, Linux / UNIX, etc.
JAP allows you to surf the net anonymously and discreetly. JAP proxies are located all over the world (JAP, 2012). You can download JAP from the site https://anon.inf.tu-dresden.de/index_en.html (see Appendix A). After downloading, follow the installation process (see Appendix B).
2.3. Blocked Websites
Companies customize their firewalls based on many factors. One of the factors is the prevention of attacks on the company's network resources. Another factor is restricting access by internal users to inappropriate or malicious websites.
In the following example, the corporate firewall denies access to the site https://www.anonymizer.com . When a user tries to open the specified site, the warning “Security risk blocked for your protection” appears in his browser window, and access to the site will be denied, see Figure 6.

Figure 6. Firewall warning about a blocked site
Determine your IP address settings. Open Windows Internet Explorer and enter [DLMURL] https://www.whatismyip.com [/ DLMURL] in the address bar. Your IP address will be displayed on the site: 45.112.164.5 (the address has been changed for security reasons), see Figure 7 (Whatismyip.com, 2012).

Figure 7. Defining an IP Address
2.4. JAP launch
To disguise your IP address, run and configure the JAP application.
Step 1: Click on the JAP application icon to start the program, see Figure 8.

Figure 8. JAP application icon
Step 2: To enable the anonymity service, click on the “On” radio button, see Figure 9.

Figure 9. JAP application interface
Step 3: From the drop-down list, select the location and anonymization server: “FreeBee-Bozlano”, see Figure 10.
Figure 10. Choosing an anonymization server
Step 4: Configure Windows Internet Explorer to use a proxy. Open Internet Explorer, click “Tools”, and then “Internet Options”, see Figure 11.

Figure 11. Configuring the proxy server in a web browser
Step 5: In the “Internet Options” window, select the “Connections” tab, and then click on the “LAN settings” button, see Figure 12.

Figure 12. Selecting LAN settings
Step 6: In the “Proxy server” field, check “Use a proxy server for your LAN”. Enter “localhost” in the address field and “4001” in the port field. To complete the setup, click the “OK” button and close the “Internet Options” window, see Figure 13.

Figure 13. Configuring the IP address and proxy port
Note: Uncheck “Use a proxy server for your LAN” when you are not working with a proxy server, otherwise normal connections will not be established.
Step 7: Test the proxy server settings. Open Internet Explorer again and enter [DLMURL] https://www.whatismyip.com [/ DLMURL] in the address bar. Now your IP address is not 45.112.164.5, but 178.33.255.188, and you are not in the United States, but in France, see Figure 14 (Whatismyip.com, 2012).

Figure 14. Checking the IP address with proxy enabled
2.5. Access blocked websites
Now in the address bar of Internet Explorer, enter the URL https://www.anonymizer.com . Now the firewall does not block the site, and we do not see any warning messages in the browser window, see Figure 15 (Anonymizer.com, 2012).

Figure 15. Accessing a blocked website using a proxy
References
Lance Cottrell, From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, (October 2, 2011). Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lance_Cottrell [/ DLMURL]
EC-Council Press, Ethical Hacking and Countermeasures, Cengage Learning (2010) Livinginternet.com, How Anonymizers Work Retrieved from https://www.livinginternet.com/i/is_anon_work.htm (2012)
Anonymizer.com, knowledgecenter, Retrieved from https://www.anonymizer.com/knowledgecenter (2012)
Fred Hapgood, Web Monitoring: Anonymizers vs. Anti-Anonymizers, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://www.csoonline.com/artic...nonymizers [/ DLMURL] (2008)
JAP, Protection of Privacy on the Internet, Retrieved from Link is not valid. de / index_en.html (2012)
JonDonym, Private and Secure Web Surfing, Retrieved from Link is not valid. net / (2012)
What is My IP, Shows Your IP Address, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://whatismyip.com [/ DLMURL] (2012) Proxify, Proxify® anonymous proxy protects your online privacy, Retrieved from https://proxify.com (2012)
Carolyn Pearson, The “Great Firewall” of China, A Real National Strategy to Secure Cyberspace ?, GIAC practical repository (2004)
Wireshark, The world's foremost network protocol analyzer, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://www.wireshark.org/ [/ DLMURL] (2012)
Websense, V-Series appliance, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://www.websense.com/content/appliances.aspx [/ DLMURL] (2012)
Network Chemistry, Inc., Packetyzer Software, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://www.gotoassist.com [/ DLMURL] (2012)
Informer Technologies, Inc., Software.informer, Network Chemistry Packetyzer, Retrieved from http: //network-chemistry-packetyzer.sof ... former.com (2012)
Microsoft Support, The Basics of Reading TCP / IP Trace, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://support.microsoft.com/kb/169292 [/ DLMURL] (2012)
Cisco, Cisco IPS 4200 Series Sensors, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://www.cisco.com/en/US/pro...ps9157/pro [/ DLMURL] duct_data_sheet09186a008014873c_ps4077_Products_Data_Sheet.html (2012)
Nevis Network, An Architectural View of LAN Security: In-Band versus Out-of-Band Solutions, Retrieved from https://www.nevisnetworks.com/content/wh ... ers / Inband% 20vs% 20 Out-of-band .pdf (2007)
Sourcefire, Snort, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://www.snort.org/ [/ DLMURL] (2012)
John Brozycki, Detecting and Preventing Anonymous Proxy Usage, [DLMURL] https://Sans.org [/ DLMURL], Reading Room (2008)
Nicholas Pappas, Network IDS & IPS Deployment Strategies, Retrieved from [DLMURL] https://www.sans.org/reading_ro...egies_2143 [/ DLMURL] (2008)
[DLMURL="https://www.securitylab.ru/analytics/436174.php"] Source [/ DLMURL] via SPKR Forum
 Original message
Original message
И большие и маленькие компании тратят огромные средства на то, чтобы быть уверенными: их сетевые ресурсы и Интернет-соединения используются по назначению. Компании нанимают лучших профессионалов в области информационных технологий, но даже самый технически непросвещенный пользователь сможет найти хитрый способ обойти политики межсетевого экрана и получить доступ к заблокированным веб-сайтам. В настоящей статье автор описывает, как анонимайзер или анонимизирующий прокси позволяет обойти политики межсетевого экрана и поставить под угрозу три главных свойства информационной безопасности сети предприятия: конфиденциальность, доступность и целостность. Но с другой стороны, анонимайзер может приносить и пользу: он помогает скрывать ваш IP-адрес при веб-сёрфинге.
1. Введение
1.1. Дилемма
И большие и маленькие компании тратят огромные средства на то, чтобы быть уверенными: их сетевые ресурсы и Интернет-соединения используются по назначению. Компании нанимают лучших профессионалов в области информационных технологий, но даже самый технически непросвещенный пользователь сможет найти хитрый способ обойти политики межсетевого экрана и получить доступ к заблокированным веб-сайтам. В настоящей статье описывает, как анонимайзер или анонимизирующий прокси позволяет обойти политики межсетевого экрана и поставить под угрозу три главных свойства информационной безопасности сети предприятия: конфиденциальность, доступность и целостность. Но с другой стороны, анонимайзер может приносить и пользу: он помогает скрывать ваш IP-адрес при веб-сёрфинге.
1.2. Вводная информация
Анонимайзеры (или анонимизирующие прокси) – это программные продукты и сервисы, которые могут приносить как пользу, так и вред. Анонимайзеры предоставляют возможность анонимно путешествовать по сети путем подмены настоящего IP-адреса пользователя. Анонимайзеры также могут обходить фильтры безопасности, установленные политиками межсетевого экрана (ACL-листы) и получать доступ к запрещенным веб-сайтам или передавать информацию без ведома организации, нарушая тем самым три основных свойства информационной безопасности.
Все, что нужно сделать пользователю, так это установить прокси-приложение и настроить в веб-браузере адрес прокси. Затем, при попытке доступа к веб-сайту, компьютер соединяется с прокси-сервером, обходит политики межсетевого экрана и заходит на заблокированный сайт.
Первый анонимайзер – Anonymizer.com – разработал в 1997 году Лэнс Котрелл в процессе работы над своей диссертацией по астрофизике в калифорнийском университете в Сан-Диего. Коттрелл ратовал за анонимность в сети, и именно он основал проект Kosovo Privacy Project, позволяющий пользователям анонимно и безнаказанно сообщать о событиях Косовской войны 1999 года (Cottrell, 2011).
С ростом популярности Интернета, все больше и больше людей относятся к сети, как к главному источнику информации. Также растет роль и коммуникационных сервисов: электронной почты, чатов, мгновенных сообщений (IM), социальных сетей (Facebook, Twitter). Электронная коммерция и онлайн-банкинг – это еще две области, которые изменили подход пользователей к ведению бизнеса и управлению своими персональными данными. Множество веб-сайтов сегодня собирают информацию о том, какие именно ресурсы посещает пользователь при путешествии по глобальной паутине. Записывается практически все: начиная от IP-адреса пользователя, заканчивая тем, сколько времени он провел на конкретном сайте. Каждый клик мыши на сайте приносит ценную (и в денежном плане тоже) информацию, за которую готовы заплатить заинтересованные компании. Многие люди уже знают, что информация о них собирается, сохраняется в cookies, а затем отправляется в коммерческие и рекламные компании типа DoubleClick или Adbot. Осторожные пользователи включают анонимизирующее программное обеспечение и сервисы, чтобы сохранять конфиденциальность и замаскировать свое реальное местоположение и IP-адрес. Еще одна причина, по которой стоит маскировать IP-адрес, заключается в том, что маскировка добавляет еще один уровень защиты от хакеров при путешествии по сети. Тем не менее, у анонимайзера есть и побочные эффекты, и этими эффектами с охотой воспользовались изобретательные пользователи: анонимайзер позволяет обойти корпоративный межсетевой экран и получить доступ к заблокированным сайтам.
На Рисунке 1 показано, как межсетевой экран блокирует сайт.

Рисунок 1. Предупреждение
На Рисунке 2 изображено, как анонимайзер обходит правила межсетевого экрана.

Рисунок 2. Обход ACL-правил
2. Принципы работы
2.1. Пример работы анонимайзера
Рабочая станция в сети, как правило, подключается к коммутатору, а коммутатор – к маршрутизатору. На маршрутизаторе для предотвращения неавторизованных подключений может быть настроен межсетевой экран или прокси-сервер. На Рисунке 3 изображена ситуация, когда пользователь со своей рабочей станции пытается открыть сайт [DLMURL]https://www.youtube.com[/DLMURL]. В ACL-правилах прописано разрешать доступ на [DLMURL]https://www.youtube.com[/DLMURL], следовательно, пользователь сможет зайти на желаемый сайт.

Рисунок 3. Разрешенные веб-сайты
На Рисунке 4 отображена обратная ситуация: доступ к [DLMURL]https://www.youtube.com[/DLMURL] запрещен. Межсетевой экран заблокирует соединение, а в веб-браузере пользователя появится соответствующее сообщение.

Рисунок 4. Запрещенные веб-сайты
На Рисунке 5 показана ситуация, когда пользователь для доступа к [DLMURL]https://www.youtube.com[/DLMURL] воспользовался Интернет-анонимайзером (прокси-сервером). Компьютер с анонимайзером устанавливают защищенное соединение, что позволяет пользователю обойти ACL-правила и свободно путешествовать по сети незаметно для межсетевого экрана. В результате межсетевой экран даже не подозревает, что пользователь заходит на заблокированные веб-сайты.

Рисунок 5. Доступ к запрещенному сайту через анонимайзер
2.2. Как осуществить задуманное
Существует множество приложений и сервисов-анонимайзеров. Некоторые из них распространяются бесплатно (например, proxify.com), за другие придется заплатить. JonDonym, к примеру, имеет месячную абонентскую плату, размер которой зависит от объема трафика. В качестве примера для настоящей статьи была выбрана бесплатная версия анонимизирующего прокси-сервера JonDonym – (JAP) AN.ON.
(JAP) AN.ON – это исследовательский, бесплатно распространяемый проект. Приложение написано на Java, благодаря чему (JAP) AN.ON можно устанавливать на различные операционные системы, в том числе и на Windows, Macintosh, OS/2, Linux/UNIX и др.
JAP позволяет анонимно и незаметно путешествовать по сети. Прокси-сервера JAP расположены по всему миру (JAP, 2012). Скачать JAP можно с сайта https://anon.inf.tu-dresden.de/index_en.html (см. Приложение А). После скачивания проследуйте по процессу установки (см. Приложение B).
2.3. Заблокированные веб-сайты
Компании настраивают свои межсетевые экраны, исходя из множества факторов. Один из факторов – предотвращение атак на сетевые ресурсы компании. Другой фактор – ограничение доступа внутренним пользователям к неприемлемым или вредоносным веб-сайтам.
В следующем примере корпоративный межсетевой экран запрещает доступ к сайту https://www.anonymizer.com. Когда пользователь пытается открыть указанный сайт, в окне его браузера появляется предупреждение “Security risk blocked for your protection”, и доступ к сайту будет запрещен, см. Рисунок 6.

Рисунок 6. Предупреждение межсетевого экрана о заблокированном сайте
Определите настройки своего IP-адреса. Откройте Windows Internet Explorer и введите [DLMURL]https://www.whatismyip.com[/DLMURL] в адресную строку. На сайте отобразится ваш IP-адрес: 45.112.164.5 (адрес в целях безопасности был изменен), см. Рисунок 7 (Whatismyip.com, 2012).

Рисунок 7. Определение IP-адреса
2.4. Запуск JAP
Для маскировки своего IP-адреса запустите и настройте приложение JAP.
Шаг 1: Кликните по иконке приложения JAP, чтобы запустить программу, см. Рисунок 8.

Рисунок 8. Иконка приложения JAP
Шаг 2: Чтобы включить службу анонимности, кликните по радиокнопке “On”, см. Рисунок 9.

Рисунок 9. Интерфейс приложения JAP
Шаг 3: Из выпадающего списка выберите местоположение и сервер анонимизации: “FreeBee-Bozlano”, см. Рисунок 10.
Рисунок 10. Выбор сервера анонимизации
Шаг 4: Настройте Windows Internet Explorer на использование прокси. Откройте Internet Explorer, кликните “Tools”, а затем “Internet Options”, см. Рисунок 11.

Рисунок 11. Настройка прокси-сервера в веб-браузере
Шаг 5: В окне “Internet Options” выберите вкладку “Connections”, а затем кликните по кнопке “LAN settings”, см. Рисунок 12.

Рисунок 12. Выбор настроек LAN
Шаг 6: В поле “Proxy server” поставьте галочку “Use a proxy server for your LAN”. В поле адреса введите “localhost”, а в поле порта “4001”. Для завершения настройки нажмите кнопку “ОК” и закройте окно “Internet Options”, см. Рисунок 13.

Рисунок 13. Настройка IP-адреса и порта прокси-сервера
Замечание: Снимайте галочку “Use a proxy server for your LAN”, когда вы не работаете с прокси-сервером, иначе обычные соединения устанавливаться не будут.
Шаг 7: Протестируем настройки прокси-сервера. Опять откройте Internet Explorer и введите [DLMURL]https://www.whatismyip.com[/DLMURL] в адресную строку. Теперь ваш IP-адрес не 45.112.164.5, а 178.33.255.188, и находитесь вы не в Соединенных Штатах, а во Франции, см. Рисунок 14 (Whatismyip.com, 2012).

Рисунок 14. Проверка IP-адреса с включенным прокси
2.5. Доступ к заблокированным веб-сайтам
Теперь в адресной строке Internet Explorer введите URL https://www.anonymizer.com. Сейчас межсетевой экран не блокирует сайт, и никакого предупреждающего сообщения в окне браузера мы не наблюдаем, см. Рисунок 15 (Anonymizer.com, 2012).

Рисунок 15. Получение доступа к заблокированному веб-сайту с помощью прокси
Ссылки
Lance Cottrell, From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, (October 2, 2011). Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lance_Cottrell[/DLMURL]
EC-Council Press, Ethical Hacking and Countermeasures, Cengage Learning (2010) Livinginternet.com, How Anonymizers Work Retrieved from https://www.livinginternet.com/i/is_anon_work.htm (2012)
Anonymizer.com, knowledgecenter, Retrieved from https://www.anonymizer.com/knowledgecenter (2012)
Fred Hapgood, Web Monitoring: Anonymizers vs. Anti-Anonymizers, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://www.csoonline.com/artic...nonymizers[/DLMURL] (2008)
JAP, Protection of Privacy on the Internet, Retrieved from Ссылка не действительна. de/index_en.html (2012)
JonDonym, Private and Secure Web Surfing, Retrieved from Ссылка не действительна. net/ (2012)
What is My IP, Shows Your IP Address, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://whatismyip.com[/DLMURL] (2012) Proxify, Proxify® anonymous proxy protects your online privacy, Retrieved from https://proxify.com (2012)
Carolyn Pearson, The “Great Firewall” of China, A Real National Strategy to Secure Cyberspace?, GIAC practical repository (2004)
Wireshark, The world’s foremost network protocol analyzer, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://www.wireshark.org/[/DLMURL] (2012)
Websense, V-Series appliance, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://www.websense.com/content/appliances.aspx[/DLMURL] (2012)
Network Chemistry, Inc., Packetyzer Software, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://www.gotoassist.com[/DLMURL] (2012)
Informer Technologies, Inc., Software.informer, Network Chemistry Packetyzer, Retrieved from https://network-chemistry-packetyzer.sof ... former.com (2012)
Microsoft Support, The Basics of Reading TCP/IP Trace, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://support.microsoft.com/kb/169292[/DLMURL] (2012)
Cisco, Cisco IPS 4200 Series Sensors, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://www.cisco.com/en/US/pro...ps9157/pro[/DLMURL] duct_data_sheet09186a008014873c_ps4077_Products_Data_Sheet.html (2012)
Nevis Network, An Architectural View of LAN Security: In-Band versus Out-of-Band Solutions, Retrieved from https://www.nevisnetworks.com/content/wh ... ers/Inband% 20vs%20Out-of-band.pdf (2007)
Sourcefire, Snort, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://www.snort.org/[/DLMURL] (2012)
John Brozycki, Detecting and Preventing Anonymous Proxy Usage, [DLMURL]https://Sans.org[/DLMURL], Reading Room (2008)
Nicholas Pappas, Network IDS & IPS Deployment Strategies, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://www.sans.org/reading_ro...egies_2143[/DLMURL] (2008)
[DLMURL="https://www.securitylab.ru/analytics/436174.php"]Источник[/DLMURL] via Форум СПКР
1. Введение
1.1. Дилемма
И большие и маленькие компании тратят огромные средства на то, чтобы быть уверенными: их сетевые ресурсы и Интернет-соединения используются по назначению. Компании нанимают лучших профессионалов в области информационных технологий, но даже самый технически непросвещенный пользователь сможет найти хитрый способ обойти политики межсетевого экрана и получить доступ к заблокированным веб-сайтам. В настоящей статье описывает, как анонимайзер или анонимизирующий прокси позволяет обойти политики межсетевого экрана и поставить под угрозу три главных свойства информационной безопасности сети предприятия: конфиденциальность, доступность и целостность. Но с другой стороны, анонимайзер может приносить и пользу: он помогает скрывать ваш IP-адрес при веб-сёрфинге.
1.2. Вводная информация
Анонимайзеры (или анонимизирующие прокси) – это программные продукты и сервисы, которые могут приносить как пользу, так и вред. Анонимайзеры предоставляют возможность анонимно путешествовать по сети путем подмены настоящего IP-адреса пользователя. Анонимайзеры также могут обходить фильтры безопасности, установленные политиками межсетевого экрана (ACL-листы) и получать доступ к запрещенным веб-сайтам или передавать информацию без ведома организации, нарушая тем самым три основных свойства информационной безопасности.
Все, что нужно сделать пользователю, так это установить прокси-приложение и настроить в веб-браузере адрес прокси. Затем, при попытке доступа к веб-сайту, компьютер соединяется с прокси-сервером, обходит политики межсетевого экрана и заходит на заблокированный сайт.
Первый анонимайзер – Anonymizer.com – разработал в 1997 году Лэнс Котрелл в процессе работы над своей диссертацией по астрофизике в калифорнийском университете в Сан-Диего. Коттрелл ратовал за анонимность в сети, и именно он основал проект Kosovo Privacy Project, позволяющий пользователям анонимно и безнаказанно сообщать о событиях Косовской войны 1999 года (Cottrell, 2011).
С ростом популярности Интернета, все больше и больше людей относятся к сети, как к главному источнику информации. Также растет роль и коммуникационных сервисов: электронной почты, чатов, мгновенных сообщений (IM), социальных сетей (Facebook, Twitter). Электронная коммерция и онлайн-банкинг – это еще две области, которые изменили подход пользователей к ведению бизнеса и управлению своими персональными данными. Множество веб-сайтов сегодня собирают информацию о том, какие именно ресурсы посещает пользователь при путешествии по глобальной паутине. Записывается практически все: начиная от IP-адреса пользователя, заканчивая тем, сколько времени он провел на конкретном сайте. Каждый клик мыши на сайте приносит ценную (и в денежном плане тоже) информацию, за которую готовы заплатить заинтересованные компании. Многие люди уже знают, что информация о них собирается, сохраняется в cookies, а затем отправляется в коммерческие и рекламные компании типа DoubleClick или Adbot. Осторожные пользователи включают анонимизирующее программное обеспечение и сервисы, чтобы сохранять конфиденциальность и замаскировать свое реальное местоположение и IP-адрес. Еще одна причина, по которой стоит маскировать IP-адрес, заключается в том, что маскировка добавляет еще один уровень защиты от хакеров при путешествии по сети. Тем не менее, у анонимайзера есть и побочные эффекты, и этими эффектами с охотой воспользовались изобретательные пользователи: анонимайзер позволяет обойти корпоративный межсетевой экран и получить доступ к заблокированным сайтам.
На Рисунке 1 показано, как межсетевой экран блокирует сайт.

Рисунок 1. Предупреждение
На Рисунке 2 изображено, как анонимайзер обходит правила межсетевого экрана.

Рисунок 2. Обход ACL-правил
2. Принципы работы
2.1. Пример работы анонимайзера
Рабочая станция в сети, как правило, подключается к коммутатору, а коммутатор – к маршрутизатору. На маршрутизаторе для предотвращения неавторизованных подключений может быть настроен межсетевой экран или прокси-сервер. На Рисунке 3 изображена ситуация, когда пользователь со своей рабочей станции пытается открыть сайт [DLMURL]https://www.youtube.com[/DLMURL]. В ACL-правилах прописано разрешать доступ на [DLMURL]https://www.youtube.com[/DLMURL], следовательно, пользователь сможет зайти на желаемый сайт.

Рисунок 3. Разрешенные веб-сайты
На Рисунке 4 отображена обратная ситуация: доступ к [DLMURL]https://www.youtube.com[/DLMURL] запрещен. Межсетевой экран заблокирует соединение, а в веб-браузере пользователя появится соответствующее сообщение.

Рисунок 4. Запрещенные веб-сайты
На Рисунке 5 показана ситуация, когда пользователь для доступа к [DLMURL]https://www.youtube.com[/DLMURL] воспользовался Интернет-анонимайзером (прокси-сервером). Компьютер с анонимайзером устанавливают защищенное соединение, что позволяет пользователю обойти ACL-правила и свободно путешествовать по сети незаметно для межсетевого экрана. В результате межсетевой экран даже не подозревает, что пользователь заходит на заблокированные веб-сайты.

Рисунок 5. Доступ к запрещенному сайту через анонимайзер
2.2. Как осуществить задуманное
Существует множество приложений и сервисов-анонимайзеров. Некоторые из них распространяются бесплатно (например, proxify.com), за другие придется заплатить. JonDonym, к примеру, имеет месячную абонентскую плату, размер которой зависит от объема трафика. В качестве примера для настоящей статьи была выбрана бесплатная версия анонимизирующего прокси-сервера JonDonym – (JAP) AN.ON.
(JAP) AN.ON – это исследовательский, бесплатно распространяемый проект. Приложение написано на Java, благодаря чему (JAP) AN.ON можно устанавливать на различные операционные системы, в том числе и на Windows, Macintosh, OS/2, Linux/UNIX и др.
JAP позволяет анонимно и незаметно путешествовать по сети. Прокси-сервера JAP расположены по всему миру (JAP, 2012). Скачать JAP можно с сайта https://anon.inf.tu-dresden.de/index_en.html (см. Приложение А). После скачивания проследуйте по процессу установки (см. Приложение B).
2.3. Заблокированные веб-сайты
Компании настраивают свои межсетевые экраны, исходя из множества факторов. Один из факторов – предотвращение атак на сетевые ресурсы компании. Другой фактор – ограничение доступа внутренним пользователям к неприемлемым или вредоносным веб-сайтам.
В следующем примере корпоративный межсетевой экран запрещает доступ к сайту https://www.anonymizer.com. Когда пользователь пытается открыть указанный сайт, в окне его браузера появляется предупреждение “Security risk blocked for your protection”, и доступ к сайту будет запрещен, см. Рисунок 6.

Рисунок 6. Предупреждение межсетевого экрана о заблокированном сайте
Определите настройки своего IP-адреса. Откройте Windows Internet Explorer и введите [DLMURL]https://www.whatismyip.com[/DLMURL] в адресную строку. На сайте отобразится ваш IP-адрес: 45.112.164.5 (адрес в целях безопасности был изменен), см. Рисунок 7 (Whatismyip.com, 2012).

Рисунок 7. Определение IP-адреса
2.4. Запуск JAP
Для маскировки своего IP-адреса запустите и настройте приложение JAP.
Шаг 1: Кликните по иконке приложения JAP, чтобы запустить программу, см. Рисунок 8.

Рисунок 8. Иконка приложения JAP
Шаг 2: Чтобы включить службу анонимности, кликните по радиокнопке “On”, см. Рисунок 9.

Рисунок 9. Интерфейс приложения JAP
Шаг 3: Из выпадающего списка выберите местоположение и сервер анонимизации: “FreeBee-Bozlano”, см. Рисунок 10.
Рисунок 10. Выбор сервера анонимизации
Шаг 4: Настройте Windows Internet Explorer на использование прокси. Откройте Internet Explorer, кликните “Tools”, а затем “Internet Options”, см. Рисунок 11.

Рисунок 11. Настройка прокси-сервера в веб-браузере
Шаг 5: В окне “Internet Options” выберите вкладку “Connections”, а затем кликните по кнопке “LAN settings”, см. Рисунок 12.

Рисунок 12. Выбор настроек LAN
Шаг 6: В поле “Proxy server” поставьте галочку “Use a proxy server for your LAN”. В поле адреса введите “localhost”, а в поле порта “4001”. Для завершения настройки нажмите кнопку “ОК” и закройте окно “Internet Options”, см. Рисунок 13.

Рисунок 13. Настройка IP-адреса и порта прокси-сервера
Замечание: Снимайте галочку “Use a proxy server for your LAN”, когда вы не работаете с прокси-сервером, иначе обычные соединения устанавливаться не будут.
Шаг 7: Протестируем настройки прокси-сервера. Опять откройте Internet Explorer и введите [DLMURL]https://www.whatismyip.com[/DLMURL] в адресную строку. Теперь ваш IP-адрес не 45.112.164.5, а 178.33.255.188, и находитесь вы не в Соединенных Штатах, а во Франции, см. Рисунок 14 (Whatismyip.com, 2012).

Рисунок 14. Проверка IP-адреса с включенным прокси
2.5. Доступ к заблокированным веб-сайтам
Теперь в адресной строке Internet Explorer введите URL https://www.anonymizer.com. Сейчас межсетевой экран не блокирует сайт, и никакого предупреждающего сообщения в окне браузера мы не наблюдаем, см. Рисунок 15 (Anonymizer.com, 2012).

Рисунок 15. Получение доступа к заблокированному веб-сайту с помощью прокси
Ссылки
Lance Cottrell, From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, (October 2, 2011). Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lance_Cottrell[/DLMURL]
EC-Council Press, Ethical Hacking and Countermeasures, Cengage Learning (2010) Livinginternet.com, How Anonymizers Work Retrieved from https://www.livinginternet.com/i/is_anon_work.htm (2012)
Anonymizer.com, knowledgecenter, Retrieved from https://www.anonymizer.com/knowledgecenter (2012)
Fred Hapgood, Web Monitoring: Anonymizers vs. Anti-Anonymizers, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://www.csoonline.com/artic...nonymizers[/DLMURL] (2008)
JAP, Protection of Privacy on the Internet, Retrieved from Ссылка не действительна. de/index_en.html (2012)
JonDonym, Private and Secure Web Surfing, Retrieved from Ссылка не действительна. net/ (2012)
What is My IP, Shows Your IP Address, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://whatismyip.com[/DLMURL] (2012) Proxify, Proxify® anonymous proxy protects your online privacy, Retrieved from https://proxify.com (2012)
Carolyn Pearson, The “Great Firewall” of China, A Real National Strategy to Secure Cyberspace?, GIAC practical repository (2004)
Wireshark, The world’s foremost network protocol analyzer, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://www.wireshark.org/[/DLMURL] (2012)
Websense, V-Series appliance, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://www.websense.com/content/appliances.aspx[/DLMURL] (2012)
Network Chemistry, Inc., Packetyzer Software, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://www.gotoassist.com[/DLMURL] (2012)
Informer Technologies, Inc., Software.informer, Network Chemistry Packetyzer, Retrieved from https://network-chemistry-packetyzer.sof ... former.com (2012)
Microsoft Support, The Basics of Reading TCP/IP Trace, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://support.microsoft.com/kb/169292[/DLMURL] (2012)
Cisco, Cisco IPS 4200 Series Sensors, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://www.cisco.com/en/US/pro...ps9157/pro[/DLMURL] duct_data_sheet09186a008014873c_ps4077_Products_Data_Sheet.html (2012)
Nevis Network, An Architectural View of LAN Security: In-Band versus Out-of-Band Solutions, Retrieved from https://www.nevisnetworks.com/content/wh ... ers/Inband% 20vs%20Out-of-band.pdf (2007)
Sourcefire, Snort, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://www.snort.org/[/DLMURL] (2012)
John Brozycki, Detecting and Preventing Anonymous Proxy Usage, [DLMURL]https://Sans.org[/DLMURL], Reading Room (2008)
Nicholas Pappas, Network IDS & IPS Deployment Strategies, Retrieved from [DLMURL]https://www.sans.org/reading_ro...egies_2143[/DLMURL] (2008)
[DLMURL="https://www.securitylab.ru/analytics/436174.php"]Источник[/DLMURL] via Форум СПКР












