Encrypted mail services: what to choose?
Konstantin Dokuchaev, author of the blog [DLMURL="https://blog.themarfa.name/"] All-in-One Person [/ DLMURL] and the telegram channel @themarfa , spoke specifically for "[DLMURL =" https://netology.ru/management/programs?utm_source=blog&utm_medium=747&utm_campaign=habr "] Netology [/ DLMURL]" about two email services: Tutanota and ProtonMail and explained which one choose and why.
Today it’s not so often that you hear about the importance of private correspondence, about the methods of protecting it and encrypting correspondence. But I still decided to take a look at two popular email services with end-to-end encryption: Tutanota and ProtonMail. They offer secure correspondence with encryption of all letters. Let's take a closer look at what both services provide and whether to hide your correspondence from the FSB or other special services and competitors.
Tutanota
Tutanota - A free mail service from the Germans, which provides encryption of mail correspondence for its customers.
Pros:
Minuses:
Registration in the service is much simpler than in regular mail providers. You only need to select the name of the mailbox and specify the password, after which you can immediately start using your new secure mail.
As can be seen from the screenshot below, Tutanota does not have a colorful interface. But this is not the main thing here. As with any email service, there is a standard distribution of letters into folders: Inbox, Drafts, Sent, Trash, Archive and Spam. When you create a new letter or reply to the received one, you will also find all the standard functions: forwarding, hidden recipients and more. You can also attach files to letters.
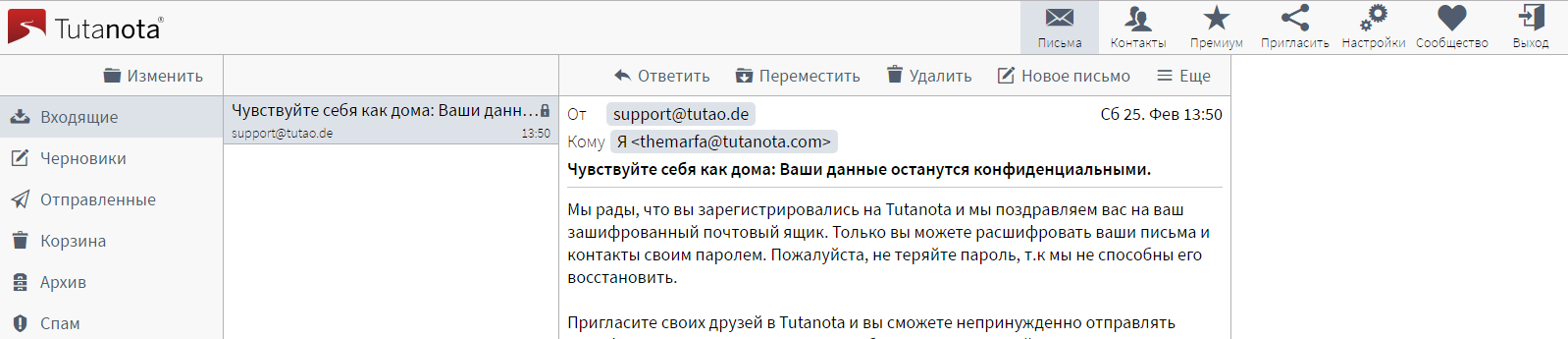
For incoming emails, you can configure filtering rules. Of the interesting things about Tutanota, it's worth noting the ability to attach multiple aliases to a single mailbox. True, such an opportunity is only available in the paid version of the service. The maximum limit on a letter with regard to attachments is 25 MB.
About security
Like most services fighting for security, Tutanota posted their source on github. Therefore, the developer community can independently check the service code for “bookmarks” and other insecure things.
Encryption and decryption of data always occurs locally on the device during authorization in the service. Your password is used as the encryption key. Therefore, you should not forget it, since even the developers are not able to help him remember. The exception is the corporate version of Tutanota. In it, the domain administrator can reset user passwords.
All correspondence is end-to-end encrypted and not transmitted to any third parties. The letters themselves are encrypted: subject, content, attachments and contact list. Tutanota only has access to the message metadata, such as the sender, recipient, and date of the message. Which, in principle, is understandable, but the developers promise in the future full encryption of letters.
Encryption of messages when sending between Tutanota users occurs using standardized AES algorithms with an encryption key of 128 bits and RSA with 2048 bits. Messages to third-party services are encrypted using AES 128 bits. The encryption algorithm is clearly shown in the picture below, where the sending and receiving letters inside and outside the service are displayed.

You can send a letter to another mail service in two ways: secure and no. Let's talk about a secure method. To send such letters you need to exchange a unique password with the recipient, which will encrypt all your correspondence. This can be done through any third-party service or orally. After the first sending the letter and entering the password by the recipient, the encryption key is stored in your address book and you can forget about it. All mail will be automatically encrypted.
Such letters cannot be viewed in standard mail clients. The recipient will receive a link by which he will be able to access the letter in the browser of a computer or smartphone.
Tutanota servers are located in Germany, which means that the service is subject to the laws of this country. But in any case, developers can’t disclose correspondence. As I said above, all correspondence is encrypted locally and a third party cannot access it.
The anonymity of the service is already visible at the registration stage, where no personal data is required from you. IP addresses are not stored by the service and are cut off when sending emails. Thus, your location is constantly hidden. For premium features you can pay with the anonymous currency Bitcoin. Of course, the service maintains technical logs for error handling. But they are stored for 14 days and do not contain any personal information about the user.
Protonmail
Now let's talk about a better-known service for secure mail exchange Protonmail .
Pros:
Minuses:
In ProtonMail during registration, no personal data is requested. You are required to select a name for the mail and specify a password with which letters will be encrypted. An optional field is an additional mail address to which you can recover your password. During the registration process, encryption keys are generated, and at the end a captcha appears to make sure your humanity.
The ProtonMail interface is less ascetic than that of its brother. Here, in addition to standard mail functions, you can find such familiar things as asterisks for selected letters and shortcuts. The interface can be customized for yourself and change the display of letters from horizontal to vertical. Letters can be sorted by various parameters. For example, by date or volume. In addition, the developers have provided a search by mail.
In general, ProtonMail is more like our usual mail services, and in its functions it is not inferior to competitors. Moving letters, viewing the "body" of the letter, convenient formatting and much more. In the service settings, you can enable two-factor authentication, disable the ability to recover a password and configure the level of logging.

About security
All data transmitted through the service is protected by encryption. The message body and attachments are end-to-end encrypted, but the subject line is not protected. This is due to the fact that developers use the PGP algorithm, which depends on the standards for transmitting data via the SMTP protocol. The developers made this concession so as not to limit the encryption of letters only between clients of the service. The PGP algorithm allows you to use correspondence regardless of the email client used.
To send letters outside the service, you can use the protected method and the unprotected one. In the first case, your letters remain end-to-end encrypted. In the second, the TLS encryption method, which supports most popular mail services, will be used to send letters. However, in this case, third parties have the opportunity to gain access to your correspondence. Moreover, all mail inside ProtonMail is not available to third parties, regardless of the method of sending letters.
ProtonMail servers are located in Switzerland and the developer is subject to the laws of this country. With a legitimate request from the court, developers are able to provide the subject of all letters.
Since the entire infrastructure of the service is based on working with the PGP algorithm, the specific encryption characteristics are not described on the developer's site. But Wikipedia knows everything:
“PGP encryption is carried out sequentially by hashing, data compression, encryption with a symmetric key, and, finally, public key encryption, and each stage can be carried out by one of several supported algorithms. Symmetric encryption is performed using one of seven symmetric algorithms (AES, CAST5, 3DES, IDEA, Twofish, Blowfish, Camellia) on the session key. A session key is generated using a cryptographically robust pseudo random number generator. The session key is encrypted with the recipient’s public key using RSA or Elgamal algorithms (depending on the type of recipient key). Each public key corresponds to a username or email address. The first version of the system was called the Trust Network and was opposed to the X.509 system, which used a hierarchical approach and was based on certification authorities, added to PGP later. Modern versions of PGP include both. ”
Which service to choose?
Both services show themselves as excellent solutions for protecting private mail correspondence, and you can choose any of them. The main parameters of choice are price and compatibility with other email clients.
A cheaper option is Tutanota. But there are several main disadvantages. First: you will not be able to use third-party email clients. Second: recipients of your letters in third-party services will be forced to read the correspondence in the browser with a password.
ProtonMail is a kind of encrypted mail for “housewives”. Minus: price. Most likely, you will have to pay for a subscription to the service. On the other hand, you will get the opportunity of "seamless" correspondence with the whole world, regardless of the mail provider or client.
From the editors
On April 21, in Netologia, the course “[DLMURL =" https://netology.ru/programs/big-data?utm_source=blog&utm_medium=747&utm_campaign=habr "] Big Data: the basics of working with large data sets [/ DLMURL]” is launched . On it we will talk about what it is, what are the methods of analysis, what are built on and how the systems work, and we will learn how to actually work with big data arrays. Working with Big Data, you can improve your skills, learn how to use data in life and work, and understand why to encrypt or not encrypt your correspondence.
Encrypted mail services: what to choose?
Konstantin Dokuchaev, author of the blog [DLMURL="https://blog.themarfa.name/"] All-in-One Person [/ DLMURL] and the telegram channel @themarfa , spoke specifically for "[DLMURL =" https://netology.ru/management/programs?utm_source=blog&utm_medium=747&utm_campaign=habr "] Netology [/ DLMURL]" about two email services: Tutanota and ProtonMail and explained which one choose and why.
Today it’s not so often that you hear about the importance of private correspondence, about the methods of protecting it and encrypting correspondence. But I still decided to take a look at two popular email services with end-to-end encryption: Tutanota and ProtonMail. They offer secure correspondence with encryption of all letters. Let's take a closer look at what both services provide and whether to hide your correspondence from the FSB or other special services and competitors.
Tutanota
Tutanota - A free mail service from the Germans, which provides encryption of mail correspondence for its customers.
Pros:
- Russian language interface.
- Simple registration.
- Free rate.
- Web version, iOS and Android.
- The ability to deploy a server on your domain.
Minuses:
- In a free account, only 1 GB of storage.
- No cloud storage support.
- No two-factor authentication.
- There is no way to receive IMAP mail by third-party clients.
Registration in the service is much simpler than in regular mail providers. You only need to select the name of the mailbox and specify the password, after which you can immediately start using your new secure mail.
As can be seen from the screenshot below, Tutanota does not have a colorful interface. But this is not the main thing here. As with any email service, there is a standard distribution of letters into folders: Inbox, Drafts, Sent, Trash, Archive and Spam. When you create a new letter or reply to the received one, you will also find all the standard functions: forwarding, hidden recipients and more. You can also attach files to letters.

For incoming emails, you can configure filtering rules. Of the interesting things about Tutanota, it's worth noting the ability to attach multiple aliases to a single mailbox. True, such an opportunity is only available in the paid version of the service. The maximum limit on a letter with regard to attachments is 25 MB.
About security
Like most services fighting for security, Tutanota posted their source on github. Therefore, the developer community can independently check the service code for “bookmarks” and other insecure things.
Encryption and decryption of data always occurs locally on the device during authorization in the service. Your password is used as the encryption key. Therefore, you should not forget it, since even the developers are not able to help him remember. The exception is the corporate version of Tutanota. In it, the domain administrator can reset user passwords.
All correspondence is end-to-end encrypted and not transmitted to any third parties. The letters themselves are encrypted: subject, content, attachments and contact list. Tutanota only has access to the message metadata, such as the sender, recipient, and date of the message. Which, in principle, is understandable, but the developers promise in the future full encryption of letters.
Encryption of messages when sending between Tutanota users occurs using standardized AES algorithms with an encryption key of 128 bits and RSA with 2048 bits. Messages to third-party services are encrypted using AES 128 bits. The encryption algorithm is clearly shown in the picture below, where the sending and receiving letters inside and outside the service are displayed.

You can send a letter to another mail service in two ways: secure and no. Let's talk about a secure method. To send such letters you need to exchange a unique password with the recipient, which will encrypt all your correspondence. This can be done through any third-party service or orally. After the first sending the letter and entering the password by the recipient, the encryption key is stored in your address book and you can forget about it. All mail will be automatically encrypted.
Such letters cannot be viewed in standard mail clients. The recipient will receive a link by which he will be able to access the letter in the browser of a computer or smartphone.
Tutanota servers are located in Germany, which means that the service is subject to the laws of this country. But in any case, developers can’t disclose correspondence. As I said above, all correspondence is encrypted locally and a third party cannot access it.
The anonymity of the service is already visible at the registration stage, where no personal data is required from you. IP addresses are not stored by the service and are cut off when sending emails. Thus, your location is constantly hidden. For premium features you can pay with the anonymous currency Bitcoin. Of course, the service maintains technical logs for error handling. But they are stored for 14 days and do not contain any personal information about the user.
Protonmail
Now let's talk about a better-known service for secure mail exchange Protonmail .
Pros:
- Web interface and mobile applications.
- Two-factor authentication.
- Fine-tuning the appearance.
- Security Settings.
- PGP encryption.
Minuses:
- There is no Russian language.
- Only 150 messages per day are available in the free version.
- The free version has 500 MB of storage.
- The restrictions are expanding, but remain even in the paid version (there is a tariff plan without restrictions).
In ProtonMail during registration, no personal data is requested. You are required to select a name for the mail and specify a password with which letters will be encrypted. An optional field is an additional mail address to which you can recover your password. During the registration process, encryption keys are generated, and at the end a captcha appears to make sure your humanity.
The ProtonMail interface is less ascetic than that of its brother. Here, in addition to standard mail functions, you can find such familiar things as asterisks for selected letters and shortcuts. The interface can be customized for yourself and change the display of letters from horizontal to vertical. Letters can be sorted by various parameters. For example, by date or volume. In addition, the developers have provided a search by mail.
In general, ProtonMail is more like our usual mail services, and in its functions it is not inferior to competitors. Moving letters, viewing the "body" of the letter, convenient formatting and much more. In the service settings, you can enable two-factor authentication, disable the ability to recover a password and configure the level of logging.

About security
All data transmitted through the service is protected by encryption. The message body and attachments are end-to-end encrypted, but the subject line is not protected. This is due to the fact that developers use the PGP algorithm, which depends on the standards for transmitting data via the SMTP protocol. The developers made this concession so as not to limit the encryption of letters only between clients of the service. The PGP algorithm allows you to use correspondence regardless of the email client used.

To send letters outside the service, you can use the protected method and the unprotected one. In the first case, your letters remain end-to-end encrypted. In the second, the TLS encryption method, which supports most popular mail services, will be used to send letters. However, in this case, third parties have the opportunity to gain access to your correspondence. Moreover, all mail inside ProtonMail is not available to third parties, regardless of the method of sending letters.
ProtonMail servers are located in Switzerland and the developer is subject to the laws of this country. With a legitimate request from the court, developers are able to provide the subject of all letters.
Since the entire infrastructure of the service is based on working with the PGP algorithm, the specific encryption characteristics are not described on the developer's site. But Wikipedia knows everything:
“PGP encryption is carried out sequentially by hashing, data compression, encryption with a symmetric key, and, finally, public key encryption, and each stage can be carried out by one of several supported algorithms. Symmetric encryption is performed using one of seven symmetric algorithms (AES, CAST5, 3DES, IDEA, Twofish, Blowfish, Camellia) on the session key. A session key is generated using a cryptographically robust pseudo random number generator. The session key is encrypted with the recipient’s public key using RSA or Elgamal algorithms (depending on the type of recipient key). Each public key corresponds to a username or email address. The first version of the system was called the Trust Network and was opposed to the X.509 system, which used a hierarchical approach and was based on certification authorities, added to PGP later. Modern versions of PGP include both. ”
Which service to choose?
Both services show themselves as excellent solutions for protecting private mail correspondence, and you can choose any of them. The main parameters of choice are price and compatibility with other email clients.
A cheaper option is Tutanota. But there are several main disadvantages. First: you will not be able to use third-party email clients. Second: recipients of your letters in third-party services will be forced to read the correspondence in the browser with a password.
ProtonMail is a kind of encrypted mail for “housewives”. Minus: price. Most likely, you will have to pay for a subscription to the service. On the other hand, you will get the opportunity of "seamless" correspondence with the whole world, regardless of the mail provider or client.
From the editors
On April 21, in Netologia, the course “[DLMURL =" https://netology.ru/programs/big-data?utm_source=blog&utm_medium=747&utm_campaign=habr "] Big Data: the basics of working with large data sets [/ DLMURL]” is launched . On it we will talk about what it is, what are the methods of analysis, what are built on and how the systems work, and we will learn how to actually work with big data arrays. Working with Big Data, you can improve your skills, learn how to use data in life and work, and understand why to encrypt or not encrypt your correspondence.
Encrypted mail services: what to choose?
 Original message
Original message
Зашифрованные почтовые сервисы: что выбрать?
Константин Докучаев, автора блога [DLMURL="https://blog.themarfa.name/"]All-in-One Person[/DLMURL] и телеграм-канала @themarfa, рассказал специально для «[DLMURL="https://netology.ru/management/programs?utm_source=blog&utm_medium=747&utm_campaign=habr"]Нетологии[/DLMURL]» о двух почтовых сервисах: Tutanota и ProtonMail и объяснил, какой из них выбрать и почему.
Сегодня уже не так часто услышишь о важности частной переписки, о методах её защиты и шифровании переписки. Но я всё равно решил взглянуть на два популярных почтовых сервиса с end-to-end шифрованием: Tutanota и ProtonMail. Они предлагают безопасную переписку с шифрованием всех писем. Давайте разберём подробно, что дают оба сервиса, и стоит ли прятать свою переписку от ФСБ или других спецслужб и конкурентов.
Tutanota
Tutanota — бесплатный почтовый сервис от немцев, который предоставляет шифрование почтовой переписки для своих клиентов.
Плюсы:
Минусы:
Регистрация в сервисе гораздо проще, чем в обычных почтовых провайдерах. От вас потребуется лишь выбрать имя почтового ящика и указать пароль, после чего сразу же можно начать пользоваться своей новой защищённой почтой.
Как видно из скриншота ниже, Tutanota не обладает красочным интерфейсом. Но не это здесь главное. Как и в любом почтовом сервисе, здесь есть стандартное распределение писем по папкам: Входящие, Черновики, Отправленные, Корзина, Архив и Спам. При создании нового письма или ответе на полученное, вы также найдёте все стандартные функции: пересылку, скрытых адресатов и прочее. Ещё можно прикреплять файлы к письмам.

Для входящих писем можете настроить правила фильтрации. Из интересных вещей в Tutanota стоить отметить возможность прикрепления нескольких псевдонимов к одному почтовому ящику. Правда, такая возможность есть только в платной версии сервиса. Максимальное ограничение на письмо с учётом вложений составляет 25 Мб.
О безопасности
Как и большинство сервисов, борющихся за безопасность, Tutanota выложили свой исходный код на Github. Поэтому сообщество разработчиков может самостоятельно проверить код сервиса на «закладки» и прочие небезопасные штуки.
Шифровка и дешифровка данных всегда происходит локально на устройства при авторизации в сервисе. В качестве ключа шифрования используется ваш пароль. Поэтому его не стоит забывать, так как даже разработчики не в состоянии помочь его вспомнить. Исключение составляет корпоративная версия Tutanota. В ней администратор домена может сбросить пароли пользователей.
Вся переписка шифруется end-to-end и не передаётся никаким третьим лицам. Шифрованию подвергаются сами письма: тема, содержимое, вложения и список контактов. Tutanota имеют доступ лишь к метаданным письма, таким как отправитель, получатель и дата письма. Что, в принципе, понятно, но разработчики обещают в будущем полное шифрование писем.
Шифрование писем при отправке между пользователями Tutanota происходит при помощи стандартизированных алгоритмов AES с ключом шифрования 128 бит и RSA с 2048 бит. Письма в сторонние сервисы шифруются при помощи AES 128 бит. Алгоритм шифрования наглядно показан на картинке ниже, где отображена отправка и получение писем внутри и вне сервиса.

Отправить письмо в другой почтовый сервис можно двумя способами: защищённым и нет. Поговорим о защищенном способе. Для отправки таких писем вам нужно обменяться с получателем уникальным паролем, которым будет зашифрована вся ваша переписка. Это можно сделать через любой сторонний сервис или устно. После первой отправки письма и ввода пароля получателем, ключ шифрования сохраняется в вашей адресной книге и про него можно забыть. Вся почта автоматически будет шифроваться.
Такие письма нельзя просмотреть в стандартных почтовых клиентах. Получателю придёт ссылка, по которой он сможет получить доступ к письму в браузере компьютера или смартфона.
Сервера Tutanota находятся в Германии, а значит, сервис подчиняется законам этой страны. Но в любом случае раскрыть переписку разработчики не могут. Как я говорил выше, вся переписка шифруется локально и третья сторона не может получить к ней доступ.
Анонимность сервиса заметна уже на этапе регистрации, где от вас не требуется никаких личных данных. IP-адреса не хранятся сервисом и обрезаются при отправке писем. Таким образом, ваше местоположение постоянно скрыто. За премиум-возможности можно заплатить анонимной валютой Bitcoin. Конечно, сервис ведёт технические логи для обработки ошибок. Но они хранятся 14 дней и не содержат никакой личной информации о пользователе.
ProtonMail
Теперь поговорим о более известном сервисе для защищённого обмена почтой ProtonMail.
Плюсы:
Минусы:
В ProtonMail при регистрации не запрашиваются никакие личные данные. От вас требуется выбрать имя для почты и указать пароль, при помощи которого будут шифроваться письма. Необязательным полем является дополнительный адрес почты, на который можно будет восстановить пароль. Во время процесса регистрации генерируются ключи шифрования, а по окончании появляется капча, чтобы убедиться в вашей человечности.
Интерфейс ProtonMail менее аскетичный, чем у своего собрата. Здесь, кроме стандартных почтовых функций, можно найти и такие уже привычные вещи, как звёздочки для избранных писем и ярлыки. Интерфейс можно настроить под себя и изменить отображение писем с горизонтального на вертикальное. Письма можно сортировать по различным параметрам. Например, по дате или объёму. Кроме этого, разработчики предусмотрели поиск по почте.
В целом ProtonMail больше похож на привычные нам почтовые сервисы, и по своим функциям он не уступает конкурентам. Перемещение писем, просмотр «тела» письма, удобное форматирование и многое другое. В настройках сервиса вы можете включить двухфакторную аутентификацию, отключить возможность восстановления пароля и настроить уровень логирования.

О безопасности
Все данные, передаваемые через сервис, защищены шифрованием. «Тело» и вложения письма зашифрованы end-to-end, но тема письма не защищена. Это сделано из-за того, что разработчики используют PGP-алгоритм, который зависит от стандартов передачи данных по протоколу SMTP. Разработчики пошли на эту уступку, чтобы не ограничивать шифрование писем только между клиентами сервиса. PGP-алгоритм позволяет пользоваться перепиской независимо от используемого почтового клиента.

Для отправки писем вне сервиса вы можете использовать защищённый метод и незащищённый. В первом случае ваши письма остаются зашифрованными end-to-end. Во втором для отправки писем будет использоваться метод шифрования TLS, который поддерживает большинство популярных почтовых сервисов. Однако в этом случае у третьих лиц появляется возможность получения доступа к вашей переписке. При этом вся почта внутри ProtonMail недоступна третьим лицам независимо от метода отправки писем.
Сервера ProtonMail находятся в Швейцарии и разработчик подчиняется законам этой страны. При законном запросе от суда разработчики в состоянии предоставить тему всех писем.
Так как вся инфраструктура сервиса базируется на работе с алгоритмом PGP, на сайте разработчика не описаны конкретные характеристики шифрования. Но Википедия всё знает:
«Шифрование PGP осуществляется последовательно хешированием, сжатием данных, шифрованием с симметричным ключом, и, наконец, шифрованием с открытым ключом, причём каждый этап может осуществляться одним из нескольких поддерживаемых алгоритмов. Симметричное шифрование производится с использованием одного из семи симметричных алгоритмов (AES, CAST5, 3DES, IDEA, Twofish, Blowfish, Camellia) на сеансовом ключе. Сеансовый ключ генерируется с использованием криптографически стойкого генератора псевдослучайных чисел. Сеансовый ключ зашифровывается открытым ключом получателя с использованием алгоритмов RSA или Elgamal (в зависимости от типа ключа получателя). Каждый открытый ключ соответствует имени пользователя или адресу электронной почты. Первая версия системы называлась Сеть Доверия и противопоставлялась системе X.509, которая использовала иерархический подход и была основана на удостоверяющих центрах, добавленный в PGP позже. Современные версии PGP включают оба способа»
Какой сервис выбрать?
Оба сервиса показывают себя как отличные решения для защиты частной почтовой переписки, и выбрать можно любой из них. В качестве основных параметров выбора остаются цена и совместимость с другими почтовыми клиентами.
Более дешёвый вариант — Tutanota. Но есть несколько главных минусов. Первый: вы не сможете пользоваться сторонними почтовыми клиентами. Второй: получатели ваших писем в сторонних сервисах будут вынуждены читать переписку в браузере с вводом пароля.
ProtonMail — своего рода шифрованная почта для «домохозяек». Минус: цена. Скорее всего, вам придётся оплатить подписку на сервис. С другой стороны, вы получите возможность «бесшовной» переписки со всем миром независимо от почтового провайдера или клиента.
От редакции
21 апреля в «Нетологии» запускается курс «[DLMURL="https://netology.ru/programs/big-data?utm_source=blog&utm_medium=747&utm_campaign=habr"]Big Data: основы работы с большими массивами данных[/DLMURL]». На нем мы расскажем о том, что же это такое, какие есть методы анализа, на чем строятся и как работают системы и научимся реальной работе с массивами больших данных. Работая с Big Data, можно повысить свою квалификацию, научиться применять в жизни и работе данные, и понять, зачем шифровать или не шифровать свои переписки.
Зашифрованные почтовые сервисы: что выбрать?
Константин Докучаев, автора блога [DLMURL="https://blog.themarfa.name/"]All-in-One Person[/DLMURL] и телеграм-канала @themarfa, рассказал специально для «[DLMURL="https://netology.ru/management/programs?utm_source=blog&utm_medium=747&utm_campaign=habr"]Нетологии[/DLMURL]» о двух почтовых сервисах: Tutanota и ProtonMail и объяснил, какой из них выбрать и почему.
Сегодня уже не так часто услышишь о важности частной переписки, о методах её защиты и шифровании переписки. Но я всё равно решил взглянуть на два популярных почтовых сервиса с end-to-end шифрованием: Tutanota и ProtonMail. Они предлагают безопасную переписку с шифрованием всех писем. Давайте разберём подробно, что дают оба сервиса, и стоит ли прятать свою переписку от ФСБ или других спецслужб и конкурентов.
Tutanota
Tutanota — бесплатный почтовый сервис от немцев, который предоставляет шифрование почтовой переписки для своих клиентов.
Плюсы:
- Русскоязычный интерфейс.
- Простая регистрация.
- Бесплатный тариф.
- Веб-версия, iOS и Android.
- Возможность развернуть сервер на своём домене.
Минусы:
- В бесплатном аккаунте только 1 Гб хранилища.
- Нет поддержки облачных хранилищ.
- Нет двухфакторной аутентификации.
- Нет возможности получения почты по IMAP сторонними клиентами.
Регистрация в сервисе гораздо проще, чем в обычных почтовых провайдерах. От вас потребуется лишь выбрать имя почтового ящика и указать пароль, после чего сразу же можно начать пользоваться своей новой защищённой почтой.
Как видно из скриншота ниже, Tutanota не обладает красочным интерфейсом. Но не это здесь главное. Как и в любом почтовом сервисе, здесь есть стандартное распределение писем по папкам: Входящие, Черновики, Отправленные, Корзина, Архив и Спам. При создании нового письма или ответе на полученное, вы также найдёте все стандартные функции: пересылку, скрытых адресатов и прочее. Ещё можно прикреплять файлы к письмам.

Для входящих писем можете настроить правила фильтрации. Из интересных вещей в Tutanota стоить отметить возможность прикрепления нескольких псевдонимов к одному почтовому ящику. Правда, такая возможность есть только в платной версии сервиса. Максимальное ограничение на письмо с учётом вложений составляет 25 Мб.
О безопасности
Как и большинство сервисов, борющихся за безопасность, Tutanota выложили свой исходный код на Github. Поэтому сообщество разработчиков может самостоятельно проверить код сервиса на «закладки» и прочие небезопасные штуки.
Шифровка и дешифровка данных всегда происходит локально на устройства при авторизации в сервисе. В качестве ключа шифрования используется ваш пароль. Поэтому его не стоит забывать, так как даже разработчики не в состоянии помочь его вспомнить. Исключение составляет корпоративная версия Tutanota. В ней администратор домена может сбросить пароли пользователей.
Вся переписка шифруется end-to-end и не передаётся никаким третьим лицам. Шифрованию подвергаются сами письма: тема, содержимое, вложения и список контактов. Tutanota имеют доступ лишь к метаданным письма, таким как отправитель, получатель и дата письма. Что, в принципе, понятно, но разработчики обещают в будущем полное шифрование писем.
Шифрование писем при отправке между пользователями Tutanota происходит при помощи стандартизированных алгоритмов AES с ключом шифрования 128 бит и RSA с 2048 бит. Письма в сторонние сервисы шифруются при помощи AES 128 бит. Алгоритм шифрования наглядно показан на картинке ниже, где отображена отправка и получение писем внутри и вне сервиса.

Отправить письмо в другой почтовый сервис можно двумя способами: защищённым и нет. Поговорим о защищенном способе. Для отправки таких писем вам нужно обменяться с получателем уникальным паролем, которым будет зашифрована вся ваша переписка. Это можно сделать через любой сторонний сервис или устно. После первой отправки письма и ввода пароля получателем, ключ шифрования сохраняется в вашей адресной книге и про него можно забыть. Вся почта автоматически будет шифроваться.
Такие письма нельзя просмотреть в стандартных почтовых клиентах. Получателю придёт ссылка, по которой он сможет получить доступ к письму в браузере компьютера или смартфона.
Сервера Tutanota находятся в Германии, а значит, сервис подчиняется законам этой страны. Но в любом случае раскрыть переписку разработчики не могут. Как я говорил выше, вся переписка шифруется локально и третья сторона не может получить к ней доступ.
Анонимность сервиса заметна уже на этапе регистрации, где от вас не требуется никаких личных данных. IP-адреса не хранятся сервисом и обрезаются при отправке писем. Таким образом, ваше местоположение постоянно скрыто. За премиум-возможности можно заплатить анонимной валютой Bitcoin. Конечно, сервис ведёт технические логи для обработки ошибок. Но они хранятся 14 дней и не содержат никакой личной информации о пользователе.
ProtonMail
Теперь поговорим о более известном сервисе для защищённого обмена почтой ProtonMail.
Плюсы:
- Веб-интерфейс и мобильные приложения.
- Двухфакторная аутентификация.
- Тонкие настройки внешнего вида.
- Настройки безопасности.
- Шифрование при помощи PGP.
Минусы:
- Нет русского языка.
- В бесплатной версии доступно лишь 150 сообщений в день.
- В бесплатной версии 500 Мб хранилища.
- Ограничения расширяются, но остаются даже в платной версии (есть тарифный план без ограничений).
В ProtonMail при регистрации не запрашиваются никакие личные данные. От вас требуется выбрать имя для почты и указать пароль, при помощи которого будут шифроваться письма. Необязательным полем является дополнительный адрес почты, на который можно будет восстановить пароль. Во время процесса регистрации генерируются ключи шифрования, а по окончании появляется капча, чтобы убедиться в вашей человечности.
Интерфейс ProtonMail менее аскетичный, чем у своего собрата. Здесь, кроме стандартных почтовых функций, можно найти и такие уже привычные вещи, как звёздочки для избранных писем и ярлыки. Интерфейс можно настроить под себя и изменить отображение писем с горизонтального на вертикальное. Письма можно сортировать по различным параметрам. Например, по дате или объёму. Кроме этого, разработчики предусмотрели поиск по почте.
В целом ProtonMail больше похож на привычные нам почтовые сервисы, и по своим функциям он не уступает конкурентам. Перемещение писем, просмотр «тела» письма, удобное форматирование и многое другое. В настройках сервиса вы можете включить двухфакторную аутентификацию, отключить возможность восстановления пароля и настроить уровень логирования.

О безопасности
Все данные, передаваемые через сервис, защищены шифрованием. «Тело» и вложения письма зашифрованы end-to-end, но тема письма не защищена. Это сделано из-за того, что разработчики используют PGP-алгоритм, который зависит от стандартов передачи данных по протоколу SMTP. Разработчики пошли на эту уступку, чтобы не ограничивать шифрование писем только между клиентами сервиса. PGP-алгоритм позволяет пользоваться перепиской независимо от используемого почтового клиента.

Для отправки писем вне сервиса вы можете использовать защищённый метод и незащищённый. В первом случае ваши письма остаются зашифрованными end-to-end. Во втором для отправки писем будет использоваться метод шифрования TLS, который поддерживает большинство популярных почтовых сервисов. Однако в этом случае у третьих лиц появляется возможность получения доступа к вашей переписке. При этом вся почта внутри ProtonMail недоступна третьим лицам независимо от метода отправки писем.
Сервера ProtonMail находятся в Швейцарии и разработчик подчиняется законам этой страны. При законном запросе от суда разработчики в состоянии предоставить тему всех писем.
Так как вся инфраструктура сервиса базируется на работе с алгоритмом PGP, на сайте разработчика не описаны конкретные характеристики шифрования. Но Википедия всё знает:
«Шифрование PGP осуществляется последовательно хешированием, сжатием данных, шифрованием с симметричным ключом, и, наконец, шифрованием с открытым ключом, причём каждый этап может осуществляться одним из нескольких поддерживаемых алгоритмов. Симметричное шифрование производится с использованием одного из семи симметричных алгоритмов (AES, CAST5, 3DES, IDEA, Twofish, Blowfish, Camellia) на сеансовом ключе. Сеансовый ключ генерируется с использованием криптографически стойкого генератора псевдослучайных чисел. Сеансовый ключ зашифровывается открытым ключом получателя с использованием алгоритмов RSA или Elgamal (в зависимости от типа ключа получателя). Каждый открытый ключ соответствует имени пользователя или адресу электронной почты. Первая версия системы называлась Сеть Доверия и противопоставлялась системе X.509, которая использовала иерархический подход и была основана на удостоверяющих центрах, добавленный в PGP позже. Современные версии PGP включают оба способа»
Какой сервис выбрать?
Оба сервиса показывают себя как отличные решения для защиты частной почтовой переписки, и выбрать можно любой из них. В качестве основных параметров выбора остаются цена и совместимость с другими почтовыми клиентами.
Более дешёвый вариант — Tutanota. Но есть несколько главных минусов. Первый: вы не сможете пользоваться сторонними почтовыми клиентами. Второй: получатели ваших писем в сторонних сервисах будут вынуждены читать переписку в браузере с вводом пароля.
ProtonMail — своего рода шифрованная почта для «домохозяек». Минус: цена. Скорее всего, вам придётся оплатить подписку на сервис. С другой стороны, вы получите возможность «бесшовной» переписки со всем миром независимо от почтового провайдера или клиента.
От редакции
21 апреля в «Нетологии» запускается курс «[DLMURL="https://netology.ru/programs/big-data?utm_source=blog&utm_medium=747&utm_campaign=habr"]Big Data: основы работы с большими массивами данных[/DLMURL]». На нем мы расскажем о том, что же это такое, какие есть методы анализа, на чем строятся и как работают системы и научимся реальной работе с массивами больших данных. Работая с Big Data, можно повысить свою квалификацию, научиться применять в жизни и работе данные, и понять, зачем шифровать или не шифровать свои переписки.
Зашифрованные почтовые сервисы: что выбрать?
Moderatör tarafında düzenlendi:












