- Joined
- Feb 17, 2007
- Messages
- 681
- Reaction score
- 1,030
- Points
- 93
Report: Slowdown of Twitter in Russia
We present to your attention the translation of the report of the international group of Internet experts Censored Planet, who spent study of the slowdown in Russia of traffic of the American social network Twitter. According to them, this will mark a new stage in the censorship of the Internet in the Russian Federation, since a centrally controlled system of influence was involved.
Among the authors of the study are experts Leonid Evdokimov and ValdikSS, collaborating with RosKomSvoboda. The project leader is Roya Ensafi from the University of Michigan.
On March 10 of this year, Russia began limit several domains associated with Twitter. In early reports, laid out on ntc.party, it has been suggested that the throttling was caused by TLS SNI targeting domains including * t.co *, * .twimg.com, and * twitter.com. The connection speed with these domains was limited to 128 kbps.
Shortly after these reports, the Russian authorities gave the official explanation for the slowdown in traffic, explaining that the state authorities "have taken measures to protect Russian citizens from the influence of illegal content", and referring to Twitter's failure to comply with requests to remove information prohibited on the territory of the Russian Federation. The incident took on a slightly larger scale than planned, in part due to the * t.co * matching rule, which inadvertently triggered regulation for unrelated high-end domains such as reddit.com or microsoft.com.
The study authors believe that:
Internet in Russia consists from thousands of autonomous systems and a large number of Internet providers, similar to the architecture of many other countries in the world. Federal Law 139-FZ, adopted in 2012, defined the policy on how Russian Internet service providers can exercise decentralized control of information.
However now appear Messages that Twitter is being blocked by another mechanism, the so-called TSPU (Threat Countermeasures). For this, DPI technology was used, on the basis of which special-purpose devices were developed by RDP.RU for Roskomnadzor. In a recent interview, Russian parliamentary deputy Alexander Khinshtein stated that Twitter throttling is the first time DPI blocks are used on a massive scale. TSPU is controlled directly and remotely by Roskomnadzor, and not by individual Internet providers, which brings the country's censorship architecture closer to the centralized models of China and Iran.
What happens when throttling (slowing down) traffic:
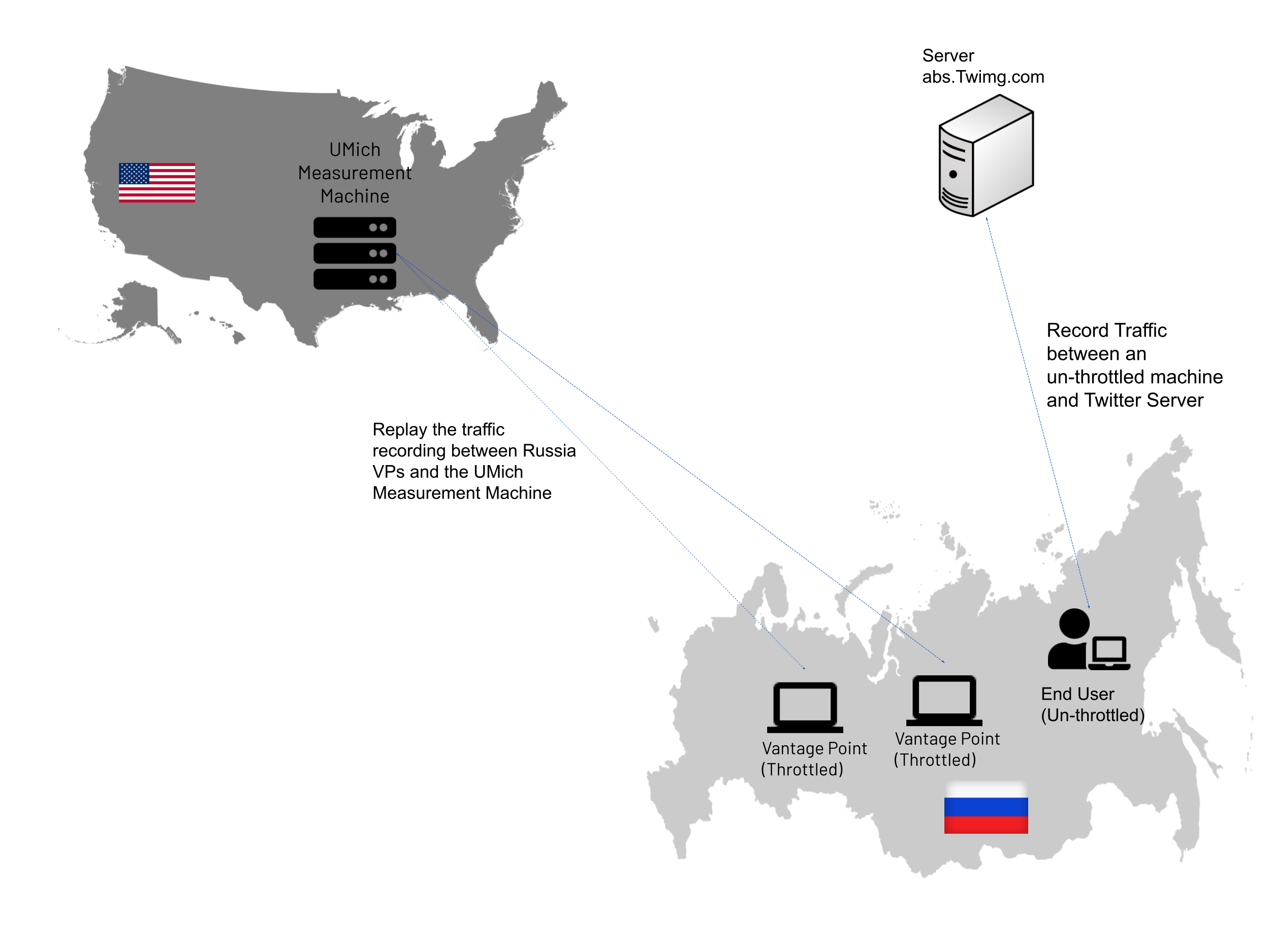
The study of Twitter throttling began on March 12, for which Censored Planet contacted Russian Internet freedom activists - they helped provide 7 observation points where attempts were recorded to slow down social network traffic: 3 regional points on landlines ( OBIT , Ufanet ) and 4 mobile viewpoints (Beeline, MTS, Tele2, Megafon), from where throttling was observed.
Having established that throttling was indeed happening, Censored Planet took deeper measurements to understand the nuances of throttling and the underlying technology. The throttling bandwidth converged to a value between 100 and 150 kbps. Throttling was done by dropping packets exceeding the rate limit (traffic control). It has also been found that the choke drops incoming data packets from any direction after the packet is overspeed.
The researchers found that some providers slowed down social network traffic slightly differently than others, but the main principle of throttling was still the same.
“Anti-censorship communities fear that governments may use throttling to restrict Internet freedom. Unfortunately, existing censorship detection platforms are focused on blocking and are not equipped to track throttling. This incident, when Russia restricted Twitter, serves as a wake-up call for censorship researchers, and we hope to spur further work to detect and circumvent this new censorship technology, ”the authors of the report conclude.
Russia is increasing pressure on social media in an effort to tighten control over sources of information that are not subordinate to the state, writes Bloomberg. Access to Twitter has been slowed for nearly a month as a Moscow supervisor demands the removal of content flagged by it as illegal - some of the posts date back to 2017, while Facebook, Telegram, TikTok and Google face fines for posts calling for protests over the imprisonment of opposition leader Alexei Navalny earlier this year.
The threat to block Twitter, the newspaper notes, arose due to the fact that Russia invested in equipment that could allow the Kremlin to cut off the country from the global Internet after a failed attempt to block the Telegram application.
According to cybersecurity researcher Leonid Evdokimov, the authorities managed to achieve a 30-40 percent success during the slowdown in Twitter activity and to eliminate the shortcomings that initially led to the freezing of websites not associated with the American social network. He also believes that shutting down Twitter has never been the goal of the Russian authorities:
We present to your attention the translation of the report of the international group of Internet experts Censored Planet, who spent study of the slowdown in Russia of traffic of the American social network Twitter. According to them, this will mark a new stage in the censorship of the Internet in the Russian Federation, since a centrally controlled system of influence was involved.
Among the authors of the study are experts Leonid Evdokimov and ValdikSS, collaborating with RosKomSvoboda. The project leader is Roya Ensafi from the University of Michigan.
On March 10 of this year, Russia began limit several domains associated with Twitter. In early reports, laid out on ntc.party, it has been suggested that the throttling was caused by TLS SNI targeting domains including * t.co *, * .twimg.com, and * twitter.com. The connection speed with these domains was limited to 128 kbps.
Shortly after these reports, the Russian authorities gave the official explanation for the slowdown in traffic, explaining that the state authorities "have taken measures to protect Russian citizens from the influence of illegal content", and referring to Twitter's failure to comply with requests to remove information prohibited on the territory of the Russian Federation. The incident took on a slightly larger scale than planned, in part due to the * t.co * matching rule, which inadvertently triggered regulation for unrelated high-end domains such as reddit.com or microsoft.com.
The study authors believe that:
This report provides current measurements and new technical details on how the regulation is implemented.“This incident represents the first known attempt by the Russian authorities to use throttling (instead of outright blocking) to pressure social networking sites. Moreover, it marks a move away from the previously decentralized model of censorship controlled by ISPs in Russia to a more centralized model that gives the authorities significant power to unilaterally impose the desired restrictions. ”
Internet in Russia consists from thousands of autonomous systems and a large number of Internet providers, similar to the architecture of many other countries in the world. Federal Law 139-FZ, adopted in 2012, defined the policy on how Russian Internet service providers can exercise decentralized control of information.
However now appear Messages that Twitter is being blocked by another mechanism, the so-called TSPU (Threat Countermeasures). For this, DPI technology was used, on the basis of which special-purpose devices were developed by RDP.RU for Roskomnadzor. In a recent interview, Russian parliamentary deputy Alexander Khinshtein stated that Twitter throttling is the first time DPI blocks are used on a massive scale. TSPU is controlled directly and remotely by Roskomnadzor, and not by individual Internet providers, which brings the country's censorship architecture closer to the centralized models of China and Iran.
What happens when throttling (slowing down) traffic:
- the retarder responds by monitoring Twitter domains in the SNI extension of the TLS client hello record;
- throttling is done through traffic control. When the throttle is triggered, data packets transmitted in any direction (upload / download) are discarded when the speed limit is reached;
- throttling devices are not located next to interlocks, suggesting they are administered separately. Deceleration devices are placed 1-2 transitions closer to end users than blocking devices;
- regulatory behavior is the same across ISPs, implying widespread deployment of a single censoring method or centralized control of regulatory devices;
- throttling can only be activated for TCP connections originating from Russia (i.e. the client is located in Russia). However, once such a connection is established, throttling can be initiated by Twitter SNI sent in any direction;
- Unlike previous reports, the relaxed governor string matching rule still applies to some domain strings, causing collateral damage, even though * t.co *, and more recently * twitter.com, have been corrected. For example, garbage.twimg.com is regulated, which means that * .twimg.com is still a matching rule;
- The choke monitors the state and resets the states for inactive connections after about 10 minutes. Apparently, as a measure against attempts to circumvent regulation, the procedure for checking each new connection in addition to the original packet is involved;
- Throttling is easily circumvented based on special session modifications, TCP fragmentation, or TLS packet filling (splitting client hello between packets);
- the report recommends that browsers and websites implement support for TLS Encrypted Client Hello (ECH and its predecessor ESNI) to make it harder for censors to throttles based on SNI;
- slowdown monitoring is challenging, and existing anti-censorship platforms are not equipped with detection and protection. The incident, in which Russia “strangled” Twitter, was a wake-up call.

The study of Twitter throttling began on March 12, for which Censored Planet contacted Russian Internet freedom activists - they helped provide 7 observation points where attempts were recorded to slow down social network traffic: 3 regional points on landlines ( OBIT , Ufanet ) and 4 mobile viewpoints (Beeline, MTS, Tele2, Megafon), from where throttling was observed.
Having established that throttling was indeed happening, Censored Planet took deeper measurements to understand the nuances of throttling and the underlying technology. The throttling bandwidth converged to a value between 100 and 150 kbps. Throttling was done by dropping packets exceeding the rate limit (traffic control). It has also been found that the choke drops incoming data packets from any direction after the packet is overspeed.
The researchers found that some providers slowed down social network traffic slightly differently than others, but the main principle of throttling was still the same.
According to them, with the proliferation of dual-use technologies, which include DPI, regulating the Internet for the authorities becomes a simple matter, but for users the task of bypassing such censorship becomes a little more difficult.“Unlike blocking, in which access to content is blocked, throttling is aimed at reducing the quality of service, which makes it almost impossible for users to distinguish imposed / deliberate slowdown from a number of nuances, such as high server load or network congestion." say researchers.
“Anti-censorship communities fear that governments may use throttling to restrict Internet freedom. Unfortunately, existing censorship detection platforms are focused on blocking and are not equipped to track throttling. This incident, when Russia restricted Twitter, serves as a wake-up call for censorship researchers, and we hope to spur further work to detect and circumvent this new censorship technology, ”the authors of the report conclude.
Russia is increasing pressure on social media in an effort to tighten control over sources of information that are not subordinate to the state, writes Bloomberg. Access to Twitter has been slowed for nearly a month as a Moscow supervisor demands the removal of content flagged by it as illegal - some of the posts date back to 2017, while Facebook, Telegram, TikTok and Google face fines for posts calling for protests over the imprisonment of opposition leader Alexei Navalny earlier this year.
The threat to block Twitter, the newspaper notes, arose due to the fact that Russia invested in equipment that could allow the Kremlin to cut off the country from the global Internet after a failed attempt to block the Telegram application.
According to cybersecurity researcher Leonid Evdokimov, the authorities managed to achieve a 30-40 percent success during the slowdown in Twitter activity and to eliminate the shortcomings that initially led to the freezing of websites not associated with the American social network. He also believes that shutting down Twitter has never been the goal of the Russian authorities:
A source"Twitter has become a kind of 'laboratory rat' for Roskomnadzor, on which he checked how well the new equipment and strategy [censoring the Network] are working."
 Original message
Original message
Доклад: Замедление Twitter в России
Представляем вашему вниманию перевод отчёта международной группы интернет-экспертов Censored Planet, которые провели исследование замедления в России трафика американской социальной сети Twitter. По их словам, это ознаменует новый этап цензуры интернета в РФ, поскольку была задействована система воздействия, управляемая централизованно.
Среди авторов исследования — сотрудничающие с «РосКомСвободой» эксперты Леонид Евдокимов и ValdikSS. Руководитель проекта — Roya Ensafi из Мичиганского Университета.
С 10 марта текущего года Россия начала ограничивать несколько доменов, связанных с Twitter. В ранних отчётах, выложенных на ntc.party, высказывалось предположение, что дросселирование было вызвано TLS SNI, нацеленным на домены, включая *t.co*, *.twimg.com и *twitter.com. Скорость соединения с этими доменами была ограничена до 128 кбит/с.
Вскоре после этих сообщений российские власти дали официальное объяснение замедления трафика, объяснив, что госудаственными органами «приняты меры для защиты российских граждан от влияния незаконного контента», и ссылаясь на невыполнение Twitter запросов на удаление запрещённой на территории РФ информации. Инцидент приобрел чуть больший, чем планировался, масштаб отчасти из-за правила сопоставления *t.co*, которое непреднамеренно активировало регулирование для несвязанных высокопрофессиональных доменов, таких как reddit.com или microsoft.com.
Авторы исследования считают, что:
Интернет в России состоит из тысяч автономных систем и большого количества интернет-провайдеров, аналогично архитектуре многих других стран мира. Федеральный закон 139-ФЗ, принятый в 2012 году, определил политику того, как российские интернет-провайдеры могут осуществлять децентрализованный контроль информации.
Однако теперь появляются сообщения о том, что Twitter блокируется с помощью другого механизма, так называемого ТСПУ (технические средства противодействия угрозам). Для этого была использована технология DPI, на базе которой для Роскомнадзора компанией RDP.RU были разработаны устройства специального назначения. В недавнем интервью депутат российского парламента Александр Хинштейн заявил, что троттлинг Twitter является первым случаем, когда блоки DPI используются в массовом масштабе. ТСПУ контролируется напрямую и удалённо Роскомнадзором, а не отдельными интернет-провайдерами, что приближает архитектуру цензуры в стране к централизованным моделям Китая и Ирана.
Что происходит при дросселировании (замедлении) трафика:

Исследование дросселирования Twitter началось 12 марта, для чего Censored Planet связалась с российскими активистами, выступающими за свободу интернета — они помогли обеспечить 7 точек наблюдения, где были зафиксированы попытки замедлить трафик соцсети: 3 региональных точки на стационарных телефонах (ОБИТ, Уфанет) и 4 мобильных точки обзора (Билайн, МТС, Теле2, Мегафон), откуда наблюдался троттлинг.
Установив, что дросселирование действительно происходит, Censored Planet провела более глубокие измерения, чтобы понять нюансы дросселирования и лежащую в его основе технологию. Пропускная способность регулирования сошлась к значению от 100 до 150 кбит/с. Регулирование происходило путем отбрасывания пакетов, превышающих ограничение скорости (контроль трафика). Также было установлено, что дроссель отбрасывает входящие пакеты данных с любого направления после превышения пакета скорости.
Исследователи установили, что у некоторых провайдеров замедление трафика соцсети происходило несколько иначе, чем у других, но главный принцип дросселирования всё равно оставался тем же.
«Сообщества по борьбе с цензурой опасаются, что государство может использовать троттлинг для ограничения свободы интернета. К сожалению, существующие платформы обнаружения цензуры сосредоточены на блокировке и не оборудованы для отслеживания троттлинга. Этот инцидент, когда Россия ограничила работу Твиттера, служит тревожным сигналом для исследователей цензуры, и мы надеемся стимулировать дальнейшую работу по обнаружению и обходу этой новой технологии цензуры», — резюмируют авторы доклада.
Россия увеличивает давление на социальные сети, стремясь к усилению контроля над источниками информации, которые не подчиняются государству, пишет Bloomberg. Доступ к Twitter был замедлен почти на месяц, так как надзорный орган в Москве требует удалить отмеченный им как незаконный контент — некоторые из публикаций относятся к 2017 году, в то время как Facebook, Telegram, TikTok и Google сталкиваются с штрафами за сообщения, призывающие к протестам из-за заключения в тюрьму лидера оппозиции Алексея Навального в начале этого года.
Угроза заблокировать Twitter, отмечает издание, возникла из-за того, что Россия вложилась в оборудование, которое может позволить Кремлю отрезать страну от глобального интернета после неудачной попытки заблокировать приложение Telegram.
По словам исследователя кибербезопасности Леонида Евдокимова, властям удалось добиться 30-40-процентного успеха во время замедления активности Twitter и устранить недостатки, которые на начальных этапах приводили к зависанию не связанных с американской соцсетью веб-сайтов. Он также считает, что отключением именно Twitter никогда не было целью российских властей:
Представляем вашему вниманию перевод отчёта международной группы интернет-экспертов Censored Planet, которые провели исследование замедления в России трафика американской социальной сети Twitter. По их словам, это ознаменует новый этап цензуры интернета в РФ, поскольку была задействована система воздействия, управляемая централизованно.
Среди авторов исследования — сотрудничающие с «РосКомСвободой» эксперты Леонид Евдокимов и ValdikSS. Руководитель проекта — Roya Ensafi из Мичиганского Университета.
С 10 марта текущего года Россия начала ограничивать несколько доменов, связанных с Twitter. В ранних отчётах, выложенных на ntc.party, высказывалось предположение, что дросселирование было вызвано TLS SNI, нацеленным на домены, включая *t.co*, *.twimg.com и *twitter.com. Скорость соединения с этими доменами была ограничена до 128 кбит/с.
Вскоре после этих сообщений российские власти дали официальное объяснение замедления трафика, объяснив, что госудаственными органами «приняты меры для защиты российских граждан от влияния незаконного контента», и ссылаясь на невыполнение Twitter запросов на удаление запрещённой на территории РФ информации. Инцидент приобрел чуть больший, чем планировался, масштаб отчасти из-за правила сопоставления *t.co*, которое непреднамеренно активировало регулирование для несвязанных высокопрофессиональных доменов, таких как reddit.com или microsoft.com.
Авторы исследования считают, что:
В этом отчёте предоставлены результаты текущих измерений и новые технические подробности о том, как реализовано регулирование.«Этот инцидент представляет собой первую известную попытку властей России использовать дросселирование (вместо прямого блокирования) для давления на сайты социальных сетей. Более того, это знаменует собой отход от ранее децентрализованной модели цензуры, контролируемой интернет-провайдерами в России, к более централизованной модели, которая дает властям значительные полномочия по одностороннему наложению желаемых ограничений».
Интернет в России состоит из тысяч автономных систем и большого количества интернет-провайдеров, аналогично архитектуре многих других стран мира. Федеральный закон 139-ФЗ, принятый в 2012 году, определил политику того, как российские интернет-провайдеры могут осуществлять децентрализованный контроль информации.
Однако теперь появляются сообщения о том, что Twitter блокируется с помощью другого механизма, так называемого ТСПУ (технические средства противодействия угрозам). Для этого была использована технология DPI, на базе которой для Роскомнадзора компанией RDP.RU были разработаны устройства специального назначения. В недавнем интервью депутат российского парламента Александр Хинштейн заявил, что троттлинг Twitter является первым случаем, когда блоки DPI используются в массовом масштабе. ТСПУ контролируется напрямую и удалённо Роскомнадзором, а не отдельными интернет-провайдерами, что приближает архитектуру цензуры в стране к централизованным моделям Китая и Ирана.
Что происходит при дросселировании (замедлении) трафика:
- замедляющее устройство реагирует, отслеживая домены Twitter в расширении SNI записи приветствия клиента TLS;
- дросселирование осуществляется с помощью контроля трафика. При срабатывании дросселя пакеты данных, передаваемые в любом направлении (загрузка/выгрузка), отбрасываются при достижении предельной скорости;
- дросселирующие устройства расположены не рядом с блокировочными устройствами, что позволяет предположить, они администрирутся отдельно. Замедляющие устройства размещаются на 1-2 перехода ближе к конечным пользователям, чем блокирующие;
- поведение регулирования одинаково у разных интернет-провайдеров, что предполагает широкое развертывание одного способа цензурирования или централизованное управление устройствами регулирования;
- регулирование может быть активировано только для TCP-соединений, исходящих из России (т.е. клиент находится в России). Однако, как только такое соединение установлено, дросселирование может быть инициировано SNI Twitter, отправленным в любом направлении;
- в отличие от предыдущих отчётов, ослабленное правило сопоставления строк регулятора все еще действует для некоторых строк домена, вызывая сопутствующий ущерб, даже несмотря на то, что *t.co*, а недавно и *twitter.com были исправлены. Например, garbage.twimg.com регулируется, что означает, что *.twimg.com всё ещё является правилом сопоставления;
- дроссель отслеживает состояние и сбрасывает состояния для неактивных подключений примерно через 10 минут. Видимо, в качестве меры против попыток обхода регулирования задействована процедура проверки каждого нового соединения помимо исходного пакета;
- регулирование легко обойти на основе специальных модификаций сеанса, фрагментации на уровне TCP или заполнения пакетов TLS (разделение приветствия клиента между пакетами);
- авторы доклада рекомендуют браузерам и веб-сайтам реализовать поддержку TLS Encrypted Client Hello (ECH и его предшественника ESNI), чтобы цензорам было труднее регулировать скорость на основе SNI;
- мониторинг замедления является сложной задачей, и существующие антицензурные платформы не оборудованы средствами обнаружения и защиты. Этот инцидент, когда Россия «задушила» Twitter, стал тревожным сигналом.

Исследование дросселирования Twitter началось 12 марта, для чего Censored Planet связалась с российскими активистами, выступающими за свободу интернета — они помогли обеспечить 7 точек наблюдения, где были зафиксированы попытки замедлить трафик соцсети: 3 региональных точки на стационарных телефонах (ОБИТ, Уфанет) и 4 мобильных точки обзора (Билайн, МТС, Теле2, Мегафон), откуда наблюдался троттлинг.
Установив, что дросселирование действительно происходит, Censored Planet провела более глубокие измерения, чтобы понять нюансы дросселирования и лежащую в его основе технологию. Пропускная способность регулирования сошлась к значению от 100 до 150 кбит/с. Регулирование происходило путем отбрасывания пакетов, превышающих ограничение скорости (контроль трафика). Также было установлено, что дроссель отбрасывает входящие пакеты данных с любого направления после превышения пакета скорости.
Исследователи установили, что у некоторых провайдеров замедление трафика соцсети происходило несколько иначе, чем у других, но главный принцип дросселирования всё равно оставался тем же.
По их словам, с распространением технологий двойного назначения, к которым относится и DPI, регулирование интернета для властей становится делом несложным, а вот пользователям задача обойти такую цензуру становится чуть сложнее.«В отличие от блокировки, при которой доступ к контенту заблокирован, дросселирование направлено на снижение качества обслуживания, что делает практически невозможным для пользователей отличить навязанное/преднамеренное замедление от ряда нюансов, например, таких как высокая нагрузка на сервер или перегрузка сети», — говорят исследователи.
«Сообщества по борьбе с цензурой опасаются, что государство может использовать троттлинг для ограничения свободы интернета. К сожалению, существующие платформы обнаружения цензуры сосредоточены на блокировке и не оборудованы для отслеживания троттлинга. Этот инцидент, когда Россия ограничила работу Твиттера, служит тревожным сигналом для исследователей цензуры, и мы надеемся стимулировать дальнейшую работу по обнаружению и обходу этой новой технологии цензуры», — резюмируют авторы доклада.
Россия увеличивает давление на социальные сети, стремясь к усилению контроля над источниками информации, которые не подчиняются государству, пишет Bloomberg. Доступ к Twitter был замедлен почти на месяц, так как надзорный орган в Москве требует удалить отмеченный им как незаконный контент — некоторые из публикаций относятся к 2017 году, в то время как Facebook, Telegram, TikTok и Google сталкиваются с штрафами за сообщения, призывающие к протестам из-за заключения в тюрьму лидера оппозиции Алексея Навального в начале этого года.
Угроза заблокировать Twitter, отмечает издание, возникла из-за того, что Россия вложилась в оборудование, которое может позволить Кремлю отрезать страну от глобального интернета после неудачной попытки заблокировать приложение Telegram.
По словам исследователя кибербезопасности Леонида Евдокимова, властям удалось добиться 30-40-процентного успеха во время замедления активности Twitter и устранить недостатки, которые на начальных этапах приводили к зависанию не связанных с американской соцсетью веб-сайтов. Он также считает, что отключением именно Twitter никогда не было целью российских властей:
Источник«Twitter стал своего рода «лабораторной крысой» для Роскомнадзора, на которой он проверил — насколько хорошо работают новое оборудование и стратегия [цензурирования Сети]».












